Responsible disclosure is a structured and ethical process designed to allow security researchers, ethical hackers, or any individual who discovers a vulnerability to inform the affected organization confidentially and securely.
The goal is to enable the organization to address and patch the vulnerability before it becomes public knowledge, thereby reducing the risk of exploitation by malicious actors. This collaborative process fosters trust between researchers and organizations, improving overall security for users and the broader community.
Key Steps in Responsible Disclosure
Managing vulnerabilities responsibly requires coordination, transparency, and legal safeguards. Consider these key phases that define a safe and effective disclosure process:
1. Discovery: A security researcher identifies a vulnerability or security weakness in software, hardware, or systems.
2. Reporting: The researcher confidentially reports the vulnerability to the affected organization or vendor, providing detailed information to replicate and understand the issue.
3. Acknowledgment & Verification: The organization acknowledges receipt of the report and verifies the existence and severity of the vulnerability.
4. Remediation: The organization develops and tests a fix or patch to resolve the vulnerability. This step may include collaborative communication to clarify details or assist in testing.
5. Disclosure: After the vulnerability is remediated and the patch deployed, the organization and researcher agree on disclosing the issue publicly. This disclosure often credits the researcher and provides information about the vulnerability and mitigation measures.
6. Safe Harbor Provisions: The organization assures the researcher that they will not face legal action if they acted responsibly and within the agreed guidelines during the discovery and reporting processes.
Importance of Responsible Disclosure
Best Practices for Organizations
Effective vulnerability disclosure strengthens organizational defenses while fostering positive external relationships. These points illustrate strategies for acknowledgment, remediation, and researcher engagement:
1. Establish a clear Vulnerability Disclosure Policy (VDP) outlining how researchers can report issues, timelines for acknowledgment and remediation, and communication protocols.
2. Provide multiple reporting channels, such as dedicated email addresses, web forms, or third-party platforms (e.g., Bugcrowd, HackerOne).
3. Set reasonable response timeframes to acknowledge reports and keep researchers informed of progress.
4. Collaborate openly with researchers, providing feedback and requesting additional information if needed.
5. Publicly recognize researchers’ contributions after successful fixes to incentivize positive engagement.
6. Maintain confidentiality throughout the process until remediation is complete.
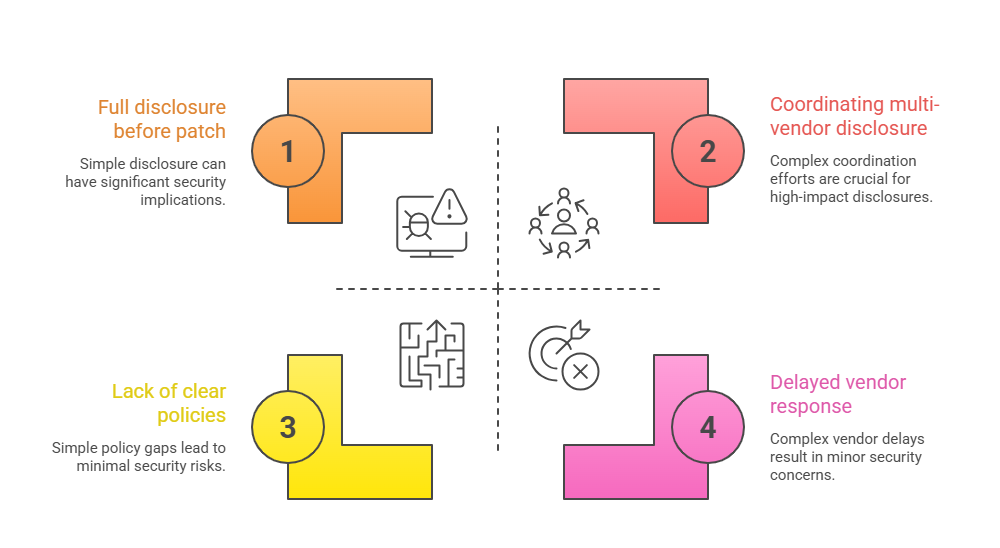
Common Challenges
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
.png)