Network mapping is the process of discovering, visualizing, and documenting the devices, connections, and overall layout of a network infrastructure. It is an essential practice in cybersecurity and network management that provides a comprehensive view of the assets, helping security professionals identify vulnerabilities and design effective defenses.
Network Mapping
Network mapping involves collecting information about connected devices, servers, routers, switches, firewalls, and the communication paths between them. The process creates diagrams or digital maps that reveal how the network is organized and where potential weaknesses may lie.
It aids in asset management by maintaining an up-to-date inventory of all network components and helps in troubleshooting connectivity and performance issues.
Importance of Network Mapping in Cybersecurity
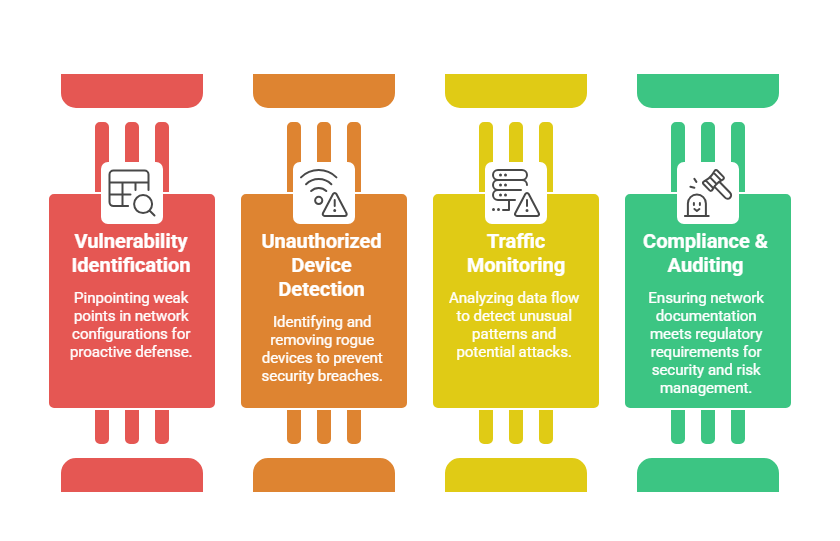 Common Network Mapping Techniques
Common Network Mapping Techniques
To gain visibility into network layouts and connected systems, analysts rely on several proven mapping approaches. Outlined here are the key methods used to discover hosts and interpret traffic flow.
1. Active Scanning: Using tools like Nmap, network scanners send probes to discover live hosts, open ports, and services. This approach is effective but may alert network defenses.
2. Passive Mapping: Employs network traffic monitoring tools (e.g., Wireshark) to glean information without actively probing the network, reducing detection risk.
3. SNMP Enumeration: Leveraging Simple Network Management Protocol to gather detailed information from network devices that support SNMP.
4. Traceroute & Ping Sweeps: Network diagnostic tools that help identify the network path and live hosts within subnet ranges.
Tools Used in Network Mapping
1. Nmap: A versatile scanning tool that discovers hosts, open ports, and service versions.
2. Wireshark: A packet analyzer used for capturing and inspecting network traffic.
3. Netdisco: A network management tool for mapping large enterprise environments.
4. SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper: Commercial software that automatically generates detailed network diagrams.
Open-source software and integrated network management suites also assist in continuous mapping and monitoring.
Network Mapping and Vulnerability Assessment
Network mapping combined with vulnerability assessment provides organizations with a comprehensive view of their security posture. By visualizing the network layout, security teams can identify critical assets where discovered vulnerabilities would pose the greatest risk.
This integrated approach allows for more effective prioritization of patches, configuration improvements, and ongoing monitoring efforts, ultimately strengthening overall defensive strategies.
Challenges and Best Practices
As networks evolve, maintaining clarity and control demands both awareness of risks and disciplined processes. Here are important issues to note along with recommended practices:
.png)
Documenting network policies and changes enhances the value of network maps.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
