Reconnaissance is a crucial phase in cybersecurity and ethical hacking where an attacker or security professional gathers information about a target system or network. It lays the foundation for planning further actions by building an understanding of the target's characteristics and vulnerabilities.
Reconnaissance can be broadly categorised into two types: passive and active. Each type has distinct methods, advantages, and risks, playing unique roles in security assessments and attacks.
Passive Reconnaissance
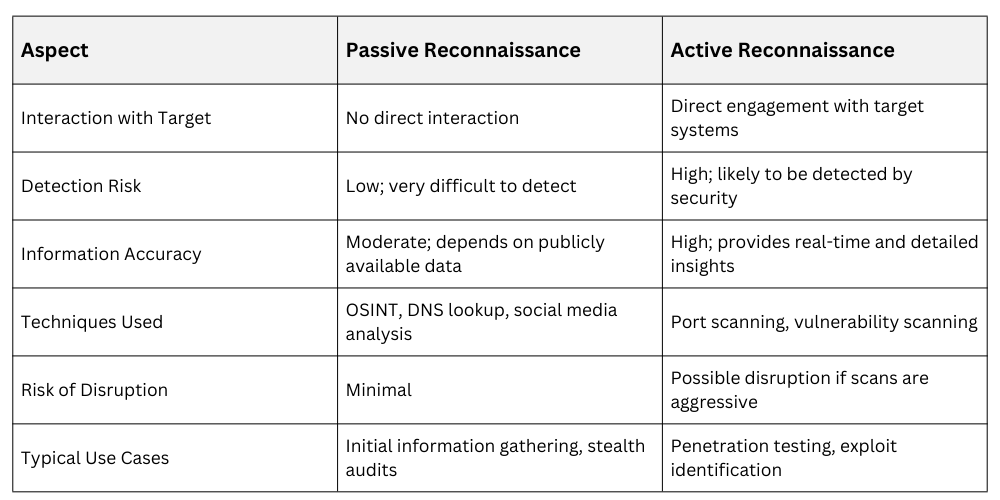
Passive reconnaissance involves collecting information about a target without directly interacting with the target system or network. It relies on publicly available data sources such as domain information, public records, social media, search engines, and organizational websites.
Techniques include DNS enumeration, WHOIS database lookups, IP address gathering, and monitoring network traffic from an external viewpoint. Because there is no direct contact with the target, passive reconnaissance is stealthy and difficult for the target to detect.
It provides an initial overview but may yield less current or detailed data compared to active methods. Passive reconnaissance is often the first step in both offensive attacks and defensive security assessments.
Active Reconnaissance
Active reconnaissance requires direct interaction with the target system or network to gather information. This method uses techniques like port scanning, ping sweeps, banner grabbing, vulnerability scanning, and traceroute analysis.
Active reconnaissance provides more detailed, real-time, and accurate data about active hosts, open ports, running services, and potential vulnerabilities. Because it interacts with the target, it is more intrusive and easier for the target's security systems, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to detect.
It carries the risk of alerting the target or even causing disruptions if improperly conducted. It is typically used after passive reconnaissance to validate findings and pinpoint attack vectors.
Comparison of Passive and Active Reconnaissance
Practical Applications
1. Attackers often begin with passive reconnaissance to avoid detection, gathering information quietly before shifting to active reconnaissance for deeper insights.
2. Security professionals use passive reconnaissance to identify publicly exposed assets and active reconnaissance to evaluate the security posture and vulnerabilities with permission.
Risks and Ethical Considerations 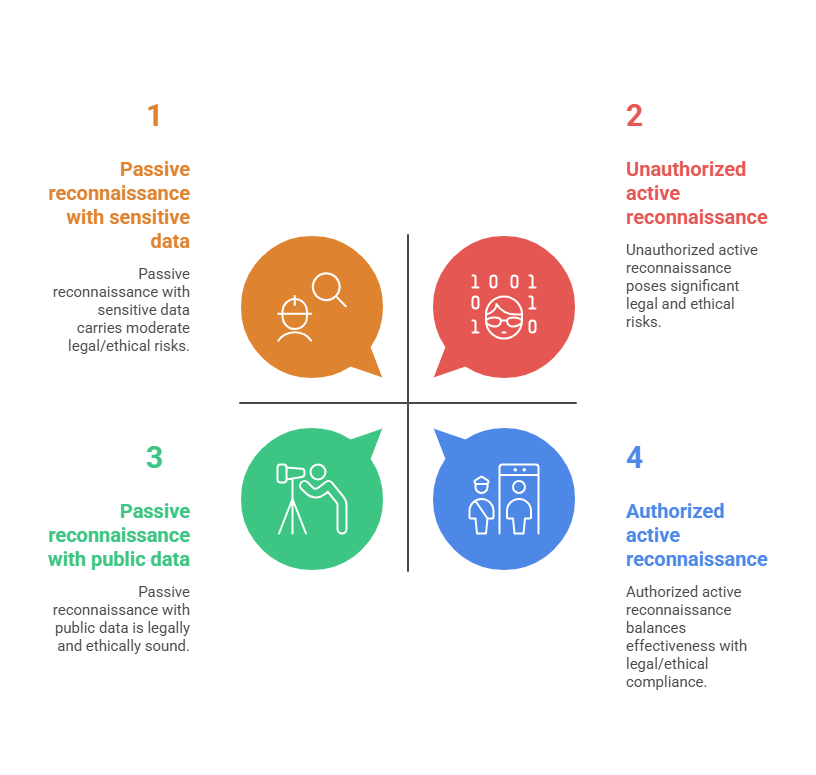
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.