In the digital age, securing user authentication is paramount to protecting sensitive information and system resources. Passwords remain the most common method for identity verification, but they must be managed securely to resist evolving cyber threats.
Secure authentication practices combine strong password policies, cryptographic protections, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring to keep accounts and systems safe from unauthorized access.
Strong Password Practices
Strong password practices are the first line of defense against unauthorized access and data breaches. Using well-structured, unique, and secure passwords significantly reduces the risk of cyberattacks and account compromise.
1. Length and Complexity: Passwords should be at least 12-16 characters, combining uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special symbols. Length significantly strengthens security.
2. Uniqueness: Each account must have a unique password to prevent a breach on one platform from affecting others.
3. Passphrases: Memorable arrangements of words (e.g., “CoffeeTableMoonWalk!”) are easier to remember and harder to crack than complex random strings.
4. Avoid Common Passwords: Ban typical weak passwords such as “123456,” “password,” or phrases that appear in breach databases.
5. Password Managers: These tools generate, store, and autofill complex passwords, minimizing reuse and weak passwords.
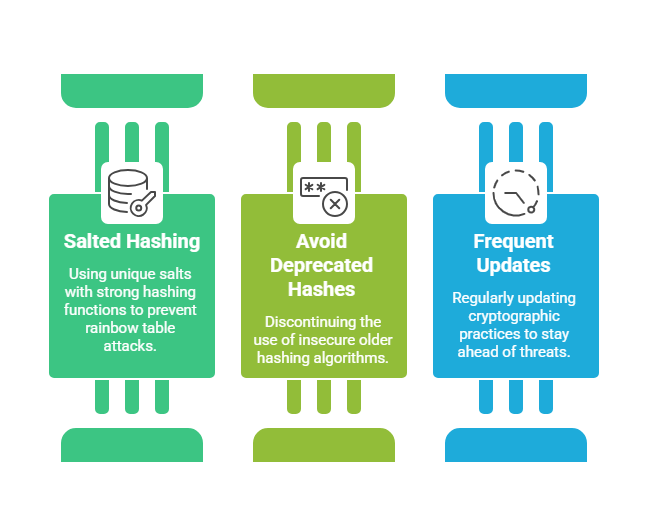
Password Storage and Hashing
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors—something they know (password), something they have (security token), or something they are (biometrics).
Benefits: Even if passwords are compromised, MFA significantly reduces unauthorized access risk.
Implementations: Common options include OTP via SMS/email/apps, hardware tokens, biometric scans (fingerprint, facial recognition), and push notification approvals.
User Education: Train users on MFA benefits and usage to improve adoption and reduce resistance.
Secure Authentication Protocols
1. Always transmit credentials over encrypted channels like HTTPS to prevent interception.
2. Use secure session management with strong, random tokens, proper expiration, and cookie protections (HttpOnly, Secure, SameSite).
3. Implement protection against brute-force attacks such as account lockouts, CAPTCHA, and rate limiting.
Monitoring and Incident Response
Effective monitoring and incident response are essential to detect and mitigate suspicious activities quickly. The following approaches help organizations identify anomalies and respond appropriately:

Emerging Trends
Passwordless authentication methods, including passkeys, biometrics, and hardware security keys, are increasingly being adopted to enhance both usability and security.
Additionally, integration with identity and access management (IAM) systems allows organizations to centralize authentication processes and enforce consistent access policies across all applications and services.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.