Network security controls are fundamental mechanisms designed to protect network resources from unauthorized access, attacks, and misuse. Among these controls, firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are key defensive technologies that form the backbone of modern network security.
Firewalls
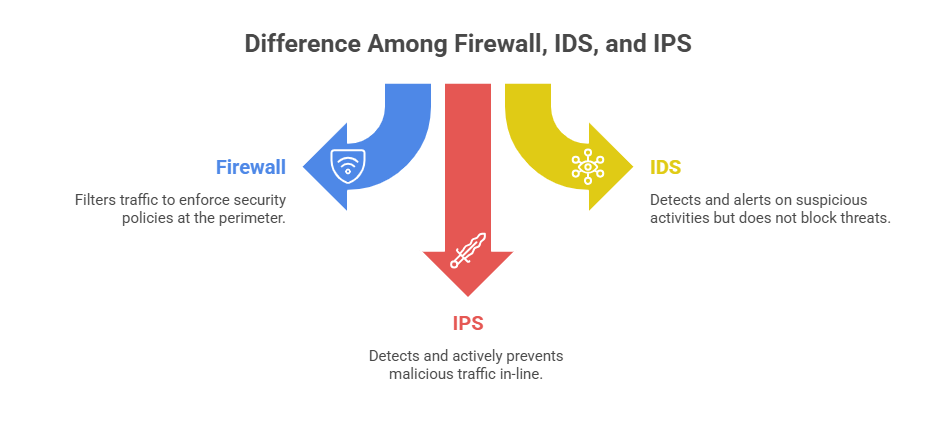
Firewalls act as the first line of defense by monitoring and controlling network traffic based on a set of predefined rules.
Functionality: They analyze incoming and outgoing packets, allowing or blocking them based on IP addresses, ports, protocols, and other criteria.
Types of Firewalls:
1. Packet-filtering firewalls, which inspect header information.
2. A stateful inspection firewall, which tracks connection states.
3. Proxy firewalls intercept and filter application-layer traffic.
4. Next-generation firewalls (NGFW) combine traditional firewall functions with deeper inspection, intrusion prevention, and application awareness.
Role: Firewalls protect network perimeters by preventing unauthorized access and limiting exposure to threats.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
IDS monitors network or system activities in real-time to detect suspicious or malicious behavior.
Functionality: It inspects network traffic or system logs and compares data against known attack signatures or anomaly patterns.
Types:
1. Network-based IDS (NIDS) monitors traffic across the entire network.
2. Host-based IDS (HIDS) monitors individual devices or servers.
Role: IDS alerts administrators to potential security incidents, enabling timely investigation and response. IDS is a passive system and does not block traffic.
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
IPS builds upon IDS functionality by actively blocking or preventing malicious traffic once detected.
Functionality: Positioned in-line with network traffic, IPS inspects packets and can terminate connections, drop malicious packets, or reconfigure firewalls automatically.
Role: IPS provides real-time protection by stopping attacks before they reach target systems, reducing damage and breach potential.
Importance of These Controls
Firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) together provide layered security that helps protect networks by preventing, detecting, and responding to threats.
By working in combination, these controls offer comprehensive visibility and management, strengthening an organization’s overall security resilience and reducing the risk of compromise.