Networking is the core technology that enables multiple computers and devices to connect and communicate, sharing data and resources. Understanding basic networking concepts such as IP addresses, MAC addresses, ports, and communication protocols is essential for anyone working with or securing computer systems. These concepts form the backbone of how digital data flows across local and global networks.
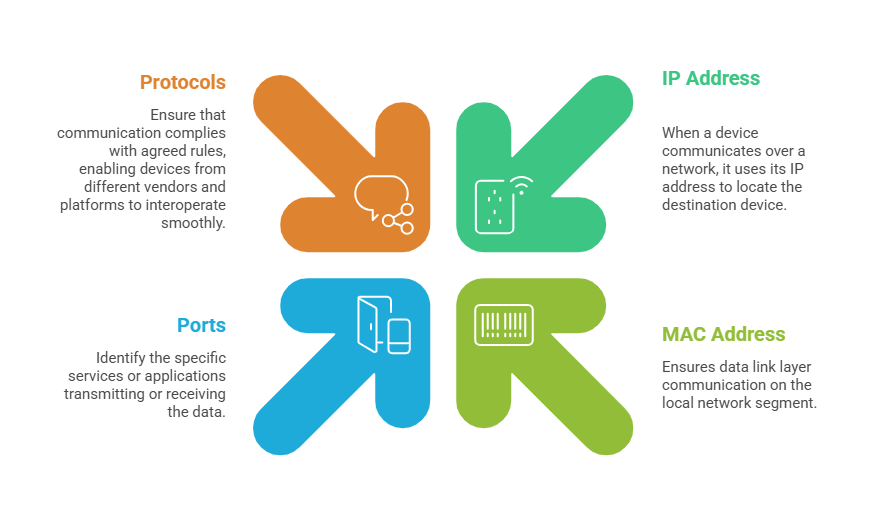
IP Address (Internet Protocol Address)
An IP address is a numerical label assigned to each device on a network. It acts as a unique identifier similar to a postal address, allowing devices to send and receive data accurately. There are two IP versions in use: IPv4 (e.g., 192.168.1.1) and IPv6, which allows for a significantly larger address space.
IP addresses are hierarchical, consisting of a network portion and a host portion, helping routers forward data efficiently across complex networks.
MAC Address (Media Access Control Address)
A MAC address is a hardware identifier permanently assigned to a network interface card (NIC) by the manufacturer. It is a unique 48-bit address, usually displayed in hexadecimal format (e.g., 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E).
MAC addresses operate at the data link layer and are used for local network communication between devices on the same physical network segment.
Ports
Ports are logical endpoints used by devices to manage multiple services and communication sessions simultaneously. Each port is identified by a number from 0 to 65535, with well-known ports such as 80 for HTTP and 443 for HTTPS.
When a device sends data, it includes the source and destination port numbers to ensure the data is delivered to the correct application or service.
Protocols
Protocols are standardised rules that govern how data is transmitted, received, and interpreted over a network. Common protocols include TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), which ensures reliable delivery, and UDP (User Datagram Protocol), which is faster but less reliable.
Other important protocols include HTTP/HTTPS for web traffic, FTP for file transfers, and DNS for resolving domain names to IP addresses.
How These Components Work Together
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.