Configuring a development stack is a fundamental step in establishing a productive and maintainable software development environment.
It involves setting up the programming languages, tools, libraries, databases, build systems, and runtime environments needed to develop, test, and deploy applications effectively.
Proper configuration ensures compatibility, simplifies dependency management, and streamlines workflows, enhancing developer efficiency and reducing integration issues.
Core Components of Development Stack Configuration
A well-structured development stack enhances efficiency and reduces configuration conflicts. The list below highlights the core components that support coding, dependency management, and environment isolation.
1. Programming Language Environment: Configure language runtimes (e.g., Python, Node.js, Java) with version managers to handle multiple versions for different projects. Example tools include pyenv for Python and nvm for Node.js.
2. Package Management: Set up package managers like npm, pip, or Maven to manage dependencies and libraries. Use lockfiles (package-lock.json, poetry.lock) to maintain reproducibility.
3. Integrated Development Environment (IDE) and Editor: Install and configure IDEs (Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ) or editors (Vim, Sublime Text) with language-specific extensions for linting, formatting, and debugging.
4. Build and Automation Tools: Configure build tools like Webpack, Gradle, or Make to automate compiling, testing, and packaging. Integrate Continuous Integration (CI) pipelines to automate testing and deployment.
5. Database Setup: Install and configure databases such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, or MongoDB with appropriate user permissions, schemas, and initial data to support development.
6. Containerization and Virtual Environments: Use Docker or virtual environments (e.g., Python virtualenv) to isolate dependencies and simulate production environments, preventing conflicts and inconsistencies.
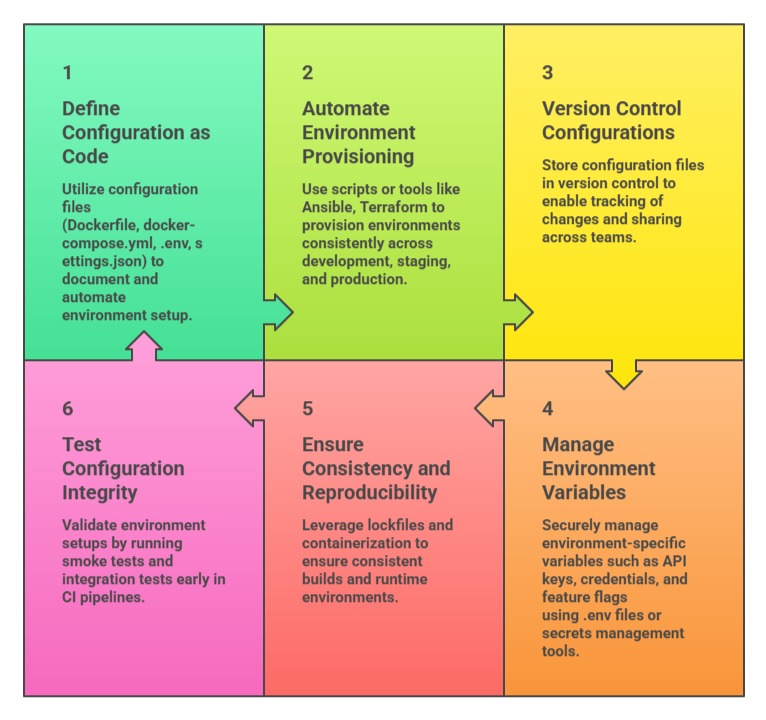
Configuration Workflow and Best Practices
A structured configuration workflow ensures environments are consistent, reproducible, and secure. The key practices listed below highlight methods for managing, automating, and validating configurations.
Example: Typical Node.js Development Stack Configuration
1. Install Node.js via nvm:
nvm install 18
nvm use 182. Initialize project and install dependencies:
npm init -y
npm install express dotenv3. Configure .env for environment variables.
4. Set up ESLint and Prettier for code quality.
5. Use Dockerfile to containerize the app.
6. Set up VS Code with relevant extensions for JavaScript and Docker.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
