Log analysis and real-time monitoring are foundational practices for maintaining the health, security, and performance of IT systems and applications.
Logs record a chronological trail of system operations, errors, and events, providing detailed insights into system behavior.
Real-time monitoring extends this by continuously observing system metrics and log entries to detect and respond to issues promptly.
Together, these practices enable proactive troubleshooting, security auditing, compliance verification, and performance optimization.
Understanding Log Files and Their Importance
Log files record detailed information about system and application activities, including kernel messages, service status updates, security alerts, and audit trails.
In Linux systems, these logs are commonly stored in the /var/log/ directory, with important files such as syslog, auth.log, kern.log, and messages capturing different types of events.
Proper log management is essential as it ensures traceability, simplifies troubleshooting, and provides reliable evidence to support security monitoring and incident investigations.
Log Analysis Techniques and Tools
Modern log analysis extends beyond individual systems to centralized and distributed environments. The key tools below show how logs can be aggregated, analyzed, and visualized across infrastructure.
1. Basic Commands
cat, less, and tail for viewing logs.
grep to filter log entries by keywords or patterns.
awk and sed for extracting and transforming data within logs.
2. Tail for Real-Time Log Viewing
tail -f /var/log/syslog continuously outputs appended log entries, useful for live monitoring.
3. Advanced Log Analyzers
Logwatch: Summarizes system logs, generating daily or weekly reports.
GoAccess: Real-time web log analyzer providing interactive dashboards.
ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana): Centralizes logs indexing, parsing, and visualizing massive log data from distributed systems.
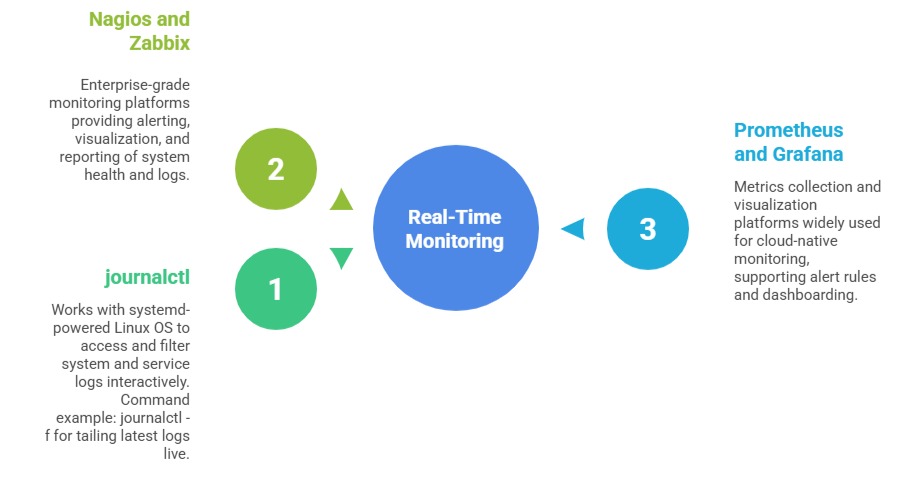
Real-Time Monitoring Tools
Real-time monitoring tools provide continuous visibility into system behavior and service health. The key tools listed below enable live log tracking, alerting, and performance visualization.
Best Practices for Effective Log Analysis and Monitoring
1. Centralize logs using syslog or specialized agents to aggregate data for easier management.
2. Set retention policies to archive or purge old logs, balancing storage and compliance needs.
3. Use consistent log formats (e.g., JSON) for better parsing and automation.
4. Implement alerting on critical log events to enable rapid response.
5. Regularly review logs to spot anomalies or early warning signs.
6. Secure log files to prevent tampering and unauthorized access.
