In modern software development and IT operations, security and vulnerability management are critical for protecting systems, applications, and data from unauthorized access, breaches, or malicious attacks.
This process involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating security weaknesses in software dependencies, configurations, and infrastructures.
Given the complexity of modern software stacks and supply chains, proactive security management ensures trustworthiness, compliance, and resilience.
Understanding Security and Vulnerabilities
Security vulnerabilities are flaws or weaknesses in systems, applications, or configurations that attackers can exploit to compromise confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
These vulnerabilities commonly arise from outdated software, misconfigurations, weak credentials, coding errors, or insecure third-party dependencies.
Attackers may exploit such weaknesses through various attack vectors, including malware, injection attacks, privilege escalation, data leaks, and denial-of-service attacks.
Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
Effective vulnerability management aligns technical risk with business impact. The key lifecycle stages below highlight how vulnerabilities are prioritized and addressed.
1. Discovery: Identify software components, versions, and configurations.
2. Assessment: Determine vulnerability severity and exploitability using CVSS scores and advisories.
3. Prioritization: Rank vulnerabilities based on impact, exploitability, and business relevance.
4. Remediation: Apply patches, updates, configuration changes, or mitigations.
5. Verification: Test fixes using automated tools or penetration testing.
6. Monitoring: Continuously monitor systems for new vulnerabilities and threats.
Key Tools and Techniques
Security assessment relies on a combination of tools and techniques to identify vulnerabilities. The key tools listed below help detect issues across code, running applications, and dependencies.
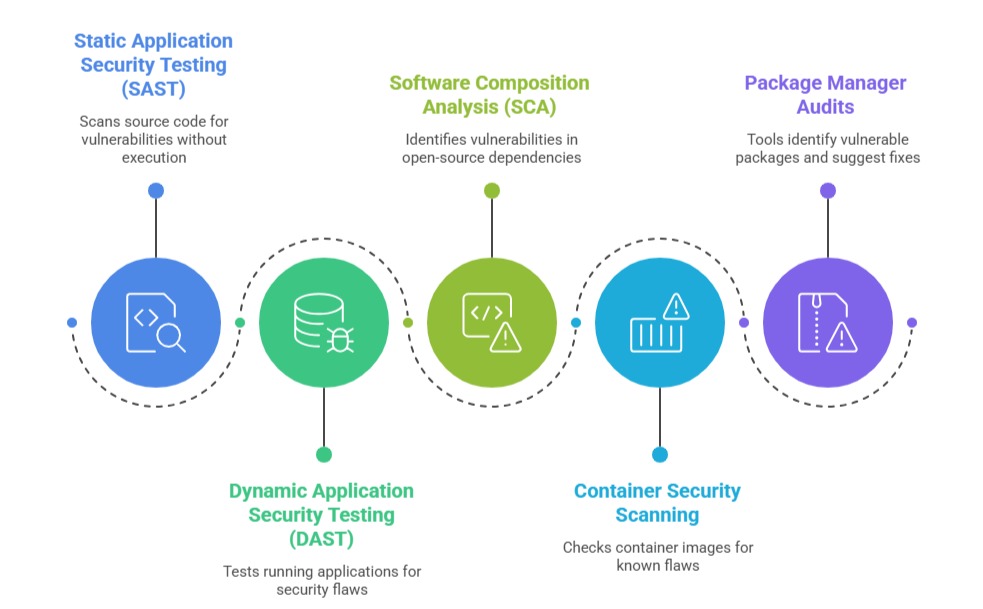
Security Tools in Package Management
Automated security tools simplify vulnerability management in package ecosystems. The list below highlights solutions that scan dependencies and assist with compliance.
npm audit: Scans Node.js projects for vulnerable dependencies and provides remediation paths.
pip-audit: Analyzes Python environments for insecure packages.
Snyk, Dependabot: Automated tools that scan repositories, alert on vulnerabilities, and prepare fix pull requests.
Best Practices for Security and Vulnerability Management
1. Maintain an updated inventory of all software components and dependencies.
2. Incorporate security scanning at early stages of the development pipeline (shift-left security).
3. Regularly update and patch dependencies and OS packages.
4. Use minimal privilege principles and secure configuration baselines.
5. Educate developers and operational teams about security hygiene.
6. Automate scanning, alerting, and remediation integrations in CI/CD pipelines.
7. Conduct frequent penetration testing and security audits.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
