Language-specific package managers are specialized tools designed to manage libraries, dependencies, and projects within a particular programming language’s ecosystem.
These package managers simplify the installation, updating, and version control of language libraries, enabling developers to build and maintain software with reliable and reproducible environments.
They resolve dependency conflicts, provide versioning mechanisms, and often integrate with build and testing tools to streamline development workflows.
Popular Language-Specific Package Managers
The main language-specific package managers enable consistent and reliable dependency management. The list below outlines widely used tools across JavaScript, Python, Rust, and Java environments.
1. npm (Node Package Manager) for JavaScript
The default package manager for Node.js projects.
Manages JavaScript libraries and depencies from the npm registry.
Supports package versioning, semantic versioning, and lockfiles (package-lock.json) for reproducible builds.
CLI commands:
npm install <package>
npm update
npm uninstall <package>Supports scripts for build, test, and start tasks.
2. Yarn for JavaScript
Alternative to npm with faster performance and secure deterministic installs.
Uses yarn.lock for dependency locking.
Compatible with npm registry.
3. Poetry for Python
Modern Python dependency management and packaging tool.
Combines virtual environment creation, dependency resolution, and packaging.
Uses pyproject.toml and poetry.lock for specification and reproducibility.
Commands:
poetry add <package>
poetry install
poetry update4. pip for Python
The original Python package installer.
Pip installs packages from the Python Package Index (PyPI).
Often used with virtual environments (venv) to isolate project packages.
Commands:
pip install <package>
pip freeze > requirements.txt
pip install -r requirements.txt5. Cargo for Rust
Rust’s package manager and build system.
Manages dependencies listed in Cargo.toml.
Support for workspaces and semantic versioning.
Commands:
cargo build
cargo test
cargo add <package>6. Maven and Gradle for Java
Build automation and dependency management tools widely used in the Java ecosystem.
Manage libraries, compile code, and run tests.
Maven uses an XML pom.xml descriptor, Gradle uses an expressive Groovy/Kotlin DSL.
Key Features of Language-Specific Package Managers
Language-specific package managers combine dependency management with environment control. The core features listed below explain how they ensure compatibility and reduce conflicts.
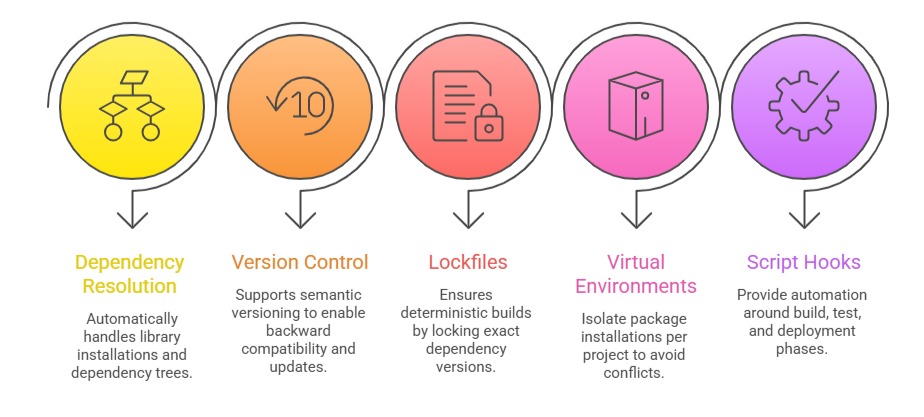
Best Practices for Managing Language Dependencies
1. Use lockfiles (package-lock.json, poetry.lock) to ensure consistent environments across machines.
2. Regularly update dependencies to incorporate security patches and features.
3. Use virtual environments to isolate project dependencies.
4. Avoid global installations for project-specific packages.
5. Audit dependencies for vulnerabilities using tools like npm audit.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
