Collaborative Git workflows are essential frameworks that enable multiple developers to work simultaneously on a shared codebase without conflicts or loss of work.
By defining clear processes for branching, committing, reviewing, and merging, teams can maintain organized, efficient, and high-quality development cycles.
Collaborative workflows emphasize transparency, code review, version control consistency, and integration automation to enhance productivity and reduce errors.
Branching for Collaboration
Developers create independent branches off the main or development branch for features, fixes, or experiments. This isolation prevents destabilizing the main production branch.
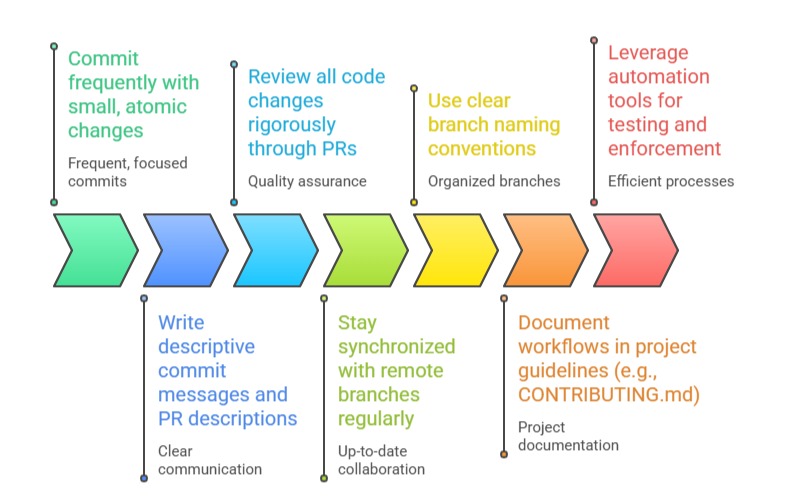
Branches have meaningful names (e.g., feature/login-system, bugfix/payment-error), improving traceability. Short-lived branches are encouraged to reduce integration complexity and merge conflicts.
Pull Requests (PRs) and Code Review
A pull request is a formal proposal to merge code changes from a feature branch into a mainline branch.
 and Code Review - visual selection-Picsart-CropImage.png)
Syncing with Remote and Managing Conflicts
Developers regularly pull changes from the main branch to keep feature branches updated, minimizing merge conflicts. When conflicts arise, developers manually resolve them locally, test thoroughly, then update the PR.
Communication during conflict resolution is vital to avoid duplicated work or introducing bugs.
Common Collaborative Workflow Models
Collaborative workflow models provide structured approaches for managing development and deployment. They help teams coordinate work, maintain code quality, and support continuous delivery.
The following models are widely adopted across modern development teams.
1. GitHub Flow
Simplified workflow with a single production branch and feature branches.
Pull requests for all changes and continuous deployment upon merge.
Best for smaller teams and continuous delivery environments.
2. Git Flow
More structured, using multiple branches: develop, release, hotfix, and features.
Facilitates scheduled releases and multiple concurrent versions.
Best suited for larger projects with formal release cycles.
3. Trunk-Based Development
Developers commit frequent, small changes directly to the main branch or short-lived branches.
Emphasizes automated testing and continuous integration.
Suits agile teams focused on rapid delivery.
Automating Collaboration with CI/CD and Hooks
Automating collaboration with CI/CD pipelines and Git hooks helps teams maintain code quality and consistency with minimal manual effort.
Continuous Integration (CI) systems automatically build and test code on every push or pull request, allowing issues to be identified and resolved early in the development process.
Git hooks further enhance automation by running client- or server-side checks such as linting, commit message validation, and test execution, ensuring team standards are enforced before code is merged.
Best Practices for Collaborative Git Workflows
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
