Choosing and configuring an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) or code editor is a foundational step in establishing an effective software development workflow.
A well-tailored IDE or editor enhances productivity by providing features like syntax highlighting, code completion, debugging tools, version control integration, and extensibility through plugins.
Proper setup ensures that the development environment aligns with project requirements, coding standards, and developer preferences.
Choosing Between IDEs and Editors
IDEs are comprehensive applications combining code editing, debugging, compiling, testing, and deployment tools in one interface. Common examples include Visual Studio Code, JetBrains IntelliJ, Eclipse, and PyCharm.
On the other hand, editors are lightweight tools primarily focused on code editing, often extensible via plugins. Examples: Vim, NeoVim, Sublime Text, Atom.
The choice depends on project complexity, language support, system resources, and personal workflow preferences.
Basic Setup Steps
Setting up a development environment involves a series of essential configuration steps. The key steps listed below help ensure productivity, consistency, and ease of development.
1. Installation:
Download from official sources or package managers.
For Linux, installation methods include apt, snap, flatpak, or manual downloads.
2. Language Support: Install language-specific extensions or plugins (e.g., Python, JavaScript, C++) to enable syntax highlighting, linting, and debugging.
3. Version Control Integration: Set up Git integration for easy commit, branching, and merge operations directly accessible in the IDE/editor.
4. Theme and Font Customization: Choose readable fonts and preferred color schemes to reduce eye strain and enhance code clarity.
5. Keybindings and Shortcuts: Customize or import keybinding sets for navigation, editing, and command execution efficiency.
6. Code Formatting and Linting: Configure automated formatting tools (e.g., Prettier, Black) and linters (e.g., ESLint, flake8) to enforce coding standards.
7. Debugger Configuration: Link IDE debugger with language runtimes and test scripts to facilitate interactive debugging.
Advanced Features and Extensions
Advanced editor features support scalable and collaborative development. The list below highlights tools for managing projects, testing, and code reuse.
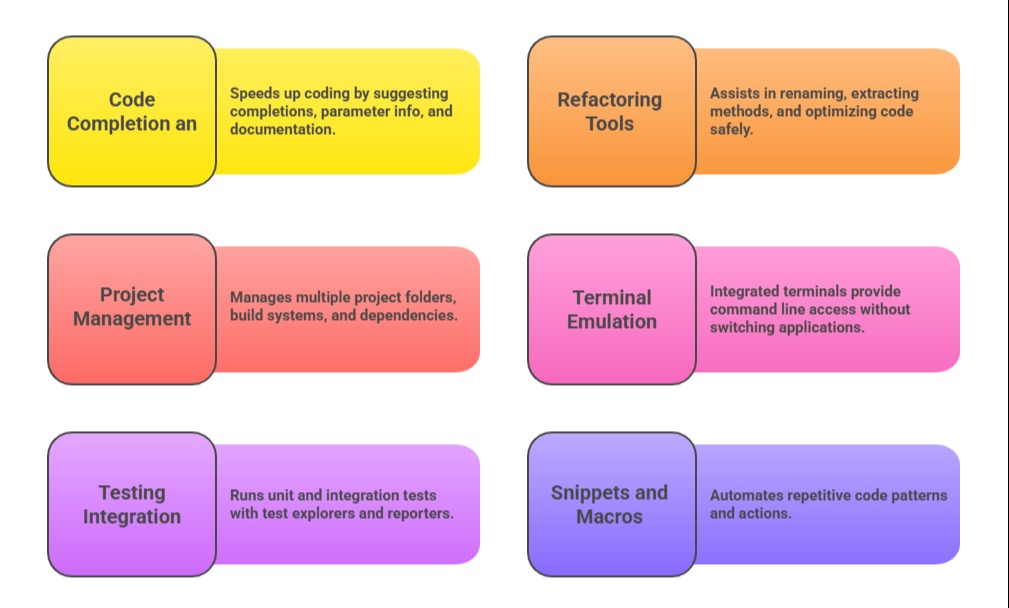
Best Practices for IDE/Editor Setup
1. Permanently save configuration files (e.g., .vscode/settings.json, .vimrc) in project repos for consistency.
2. Use workspace settings to manage project-specific preferences.
3. Update tools and extensions regularly for security and features.
4. Leverage cloud backup or synchronization to preserve personalized setups.
5. Customize based on hardware capabilities; favor lightweight editors on constrained systems.
