An interactive shell is a command-line interface that allows users to enter commands and receive immediate feedback, making it the primary way developers and system administrators interact with Linux systems.
Modern interactive shells, such as Bash, Zsh, and Fish, offer a plethora of features designed to boost productivity and streamline command execution.
Features like command history navigation, auto-completion, keyboard shortcuts, aliases, and search functions reduce typing effort and speed up workflow.
Command History Navigation and Search
One of the fundamental productivity features is the command history, which records previously entered commands, allowing quick reuse and modification.
1. Arrow Keys: Pressing the up and down arrow keys cycles through command history for easy editing.
2. Ctrl + R: Initiates a reverse search, allowing users to search for commands containing specific substrings interactively.
3. History Command: Typing history lists all previous commands with line numbers.
4. Executing Previous Commands: Using !n executes the command at position n in history; !! repeats the last command.
These features minimize repetitive typing and help recover complex or rarely used commands quickly.
Auto-Completion and Command Suggestions
Auto-completion reduces typing by completing commands, filenames, and variable names as the user types.

This speeds up command typing and reduces errors from manual input.
Keyboard Shortcuts and Editing
Interactive shells support a wide array of keyboard shortcuts improving text editing in the command line.
Ctrl + A: Move cursor to beginning of the line.
Ctrl + E: Move cursor to end of the line.
Ctrl + U: Clear the line from the cursor to the beginning.
Ctrl + K: Clear the line from the cursor to the end.
Ctrl + W: Delete the word before the cursor.
Ctrl + L: Clear the terminal screen (similar to the clear command).
These shortcuts facilitate quick command modifications and navigation within the terminal.
Aliases and Functions for Efficiency
Users can define aliases—shortcuts for long or frequently used commands—and functions, reusable scripts encapsulating complex logic, to save time.
Example aliases:
alias gs='git status'
alias ll='ls -alF'Example function to create and change to a directory:
mkcd () {
mkdir -p "$1"
cd "$1"
}These custom commands reduce repetitive typing and simplify complex workflows.
Multiple Tab Completion and Menu Selection
Some shells support multiple tab completions with a menu interface.
1. Pressing Tab twice shows all possible completions to choose from.
2. Interactive menus allow cycling through options using arrow keys, enabling easy selection without typing full strings.
Prompt Customization for Context
Interactive prompts can display contextual information such as current directory, git branch status, user, hostname, and command execution status.
1. Prompts inform users about their environment at a glance.
2. Customized prompts using frameworks (Powerlevel10k, Oh My Zsh) enhance usability and aesthetics.
Background Jobs and Job Control
Users can manage running processes directly from the shell:
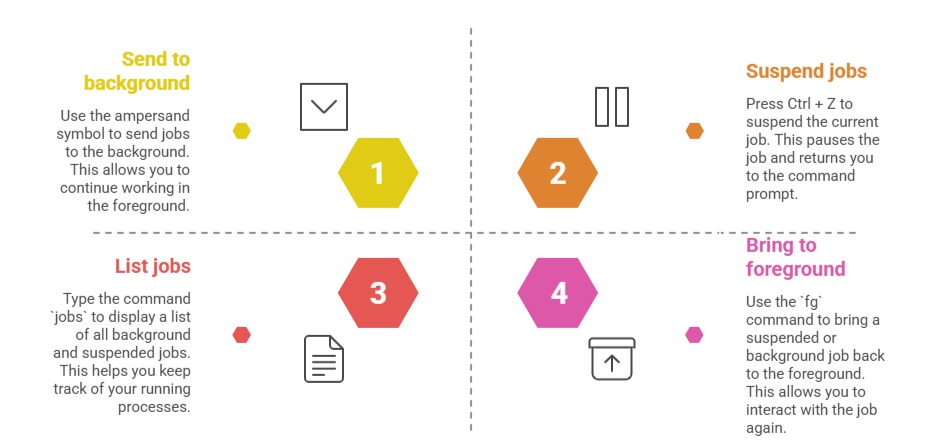
These features allow multitasking within the terminal environment.
