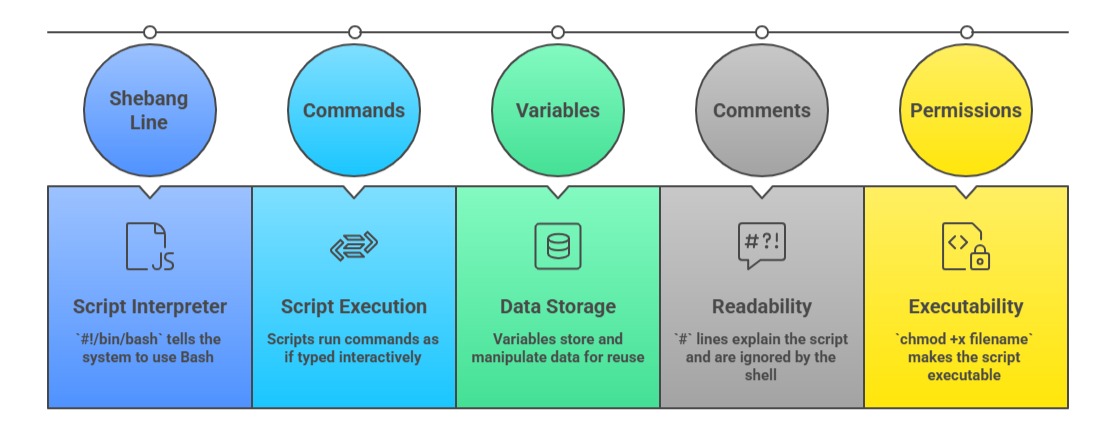
Shell scripting is a powerful method to automate tasks and orchestrate system commands in Unix-like operating systems such as Linux. A shell script is a plain text file containing a sequence of commands that the shell interpreter executes.
Shell scripting simplifies repetitive tasks, improves efficiency, and enables complex workflows by leveraging conditional logic, loops, variables, and functions.
What is a Shell Script?
A shell script contains commands that run sequentially in a shell environment like Bash. Scripts have executable permissions and often start with a shebang (#!) line to specify the interpreter.
Writing shell scripts allows automating operations such as file management, system monitoring, application deployment, and more.
Example shebang and simple script:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello, World!"Save as hello.sh, give execute permission (chmod +x hello.sh), and run with ./hello.sh.
Script Structure and Execution
Variables and Parameters
Variables store strings, numbers, or command outputs.
Assign without spaces: var="value".
Access with a dollar sign: echo $var.
Special variables:
$0 – script name
$1, $2,... – arguments passed to the script
$# – number of arguments
$? – exit status of last command
Example:
if [ "$1" == "start" ]; then
echo "Starting service"
else
echo "Unknown command"
fiControl Structures: Conditional Statements and Loops
- If-else statements control decision-making:
if [ "$1" == "start" ]; then
echo "Starting service"
else
echo "Unknown command"
fi- For loops iterate over a list:
for file in *.txt; do
echo "Processing $file"
done- While loops run based on a condition:
count=1
while [ $count -le 5 ]; do
echo "Count: $count"
((count++))
doneFunctions in Shell Scripts
Functions group commands for reuse, improving script clarity and modularity.
function greet() {
echo "Hello, $1"
}
greet "Alice"Functions support parameters and local variables and can be called multiple times.
Input and Output
1. Use read to take user input:
read -p "Enter your name: " name
echo "Hello, $name"2. Output can be printed using echo or printf.
3. Redirect output to files using > (overwrite) or >> (append).
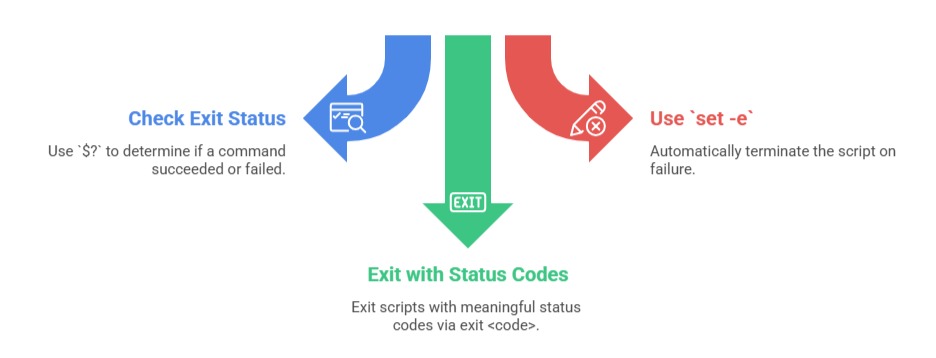
Error Handling and Exit Status
Debugging Tips
1. Add set -x to enable command tracing.
2. Use echo for logging variable state.
3. Test scripts incrementally.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.