Maintaining high code quality alongside robust security practices is indispensable for developing reliable, secure, and maintainable software applications.
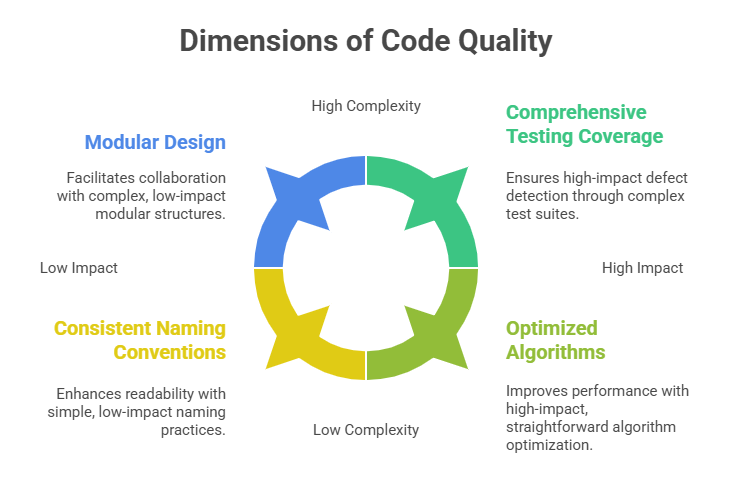
Code quality encompasses attributes like correctness, readability, modularity, and performance, while security best practices aim to protect applications from vulnerabilities and unauthorized access.
Together, these practices ensure that software not only meets functional requirements but also withstands evolving threats and scaling challenges.
Adopting industry-proven guidelines, automated tools, and team-driven standards supports sustainable development and operational excellence.
Security Best Practices in Development
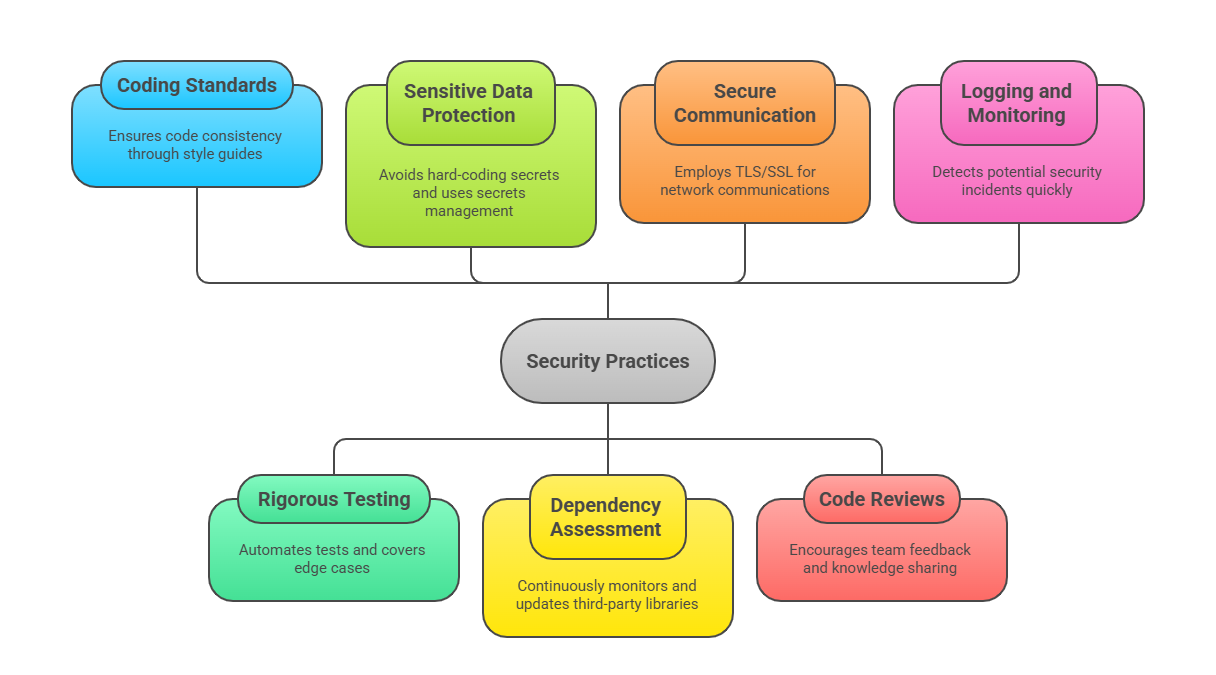
Security must be a core part of the software development lifecycle, not an afterthought. Below are key practices developers should follow to safeguard applications from common threats and exploits.
1. Secure Coding Guidelines: Follow standards such as OWASP Top Ten to avoid common vulnerabilities, including injection flaws, broken authentication, and cross-site scripting.
2. Input Validation and Sanitization: Validate all input to prevent malicious data from compromising the system.
3. Authentication and Authorization: Implement strong identity management and enforce least privilege principles.
4. Data Protection: Use encryption in transit and at rest; avoid hard-coded secrets.
5. Dependency Management: Regularly audit third-party libraries for vulnerabilities and apply timely updates.
Tools and Techniques to Enforce Quality and Security
Maintaining high standards of code quality and security requires automation, collaboration, and continuous monitoring. The following tools and techniques help integrate these principles directly into the development lifecycle.
1. Static Application Security Testing (SAST): Analyze source code for security flaws early in the development cycle.
2. Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): Test running applications against known vulnerabilities.
3. Code Review Practices: Peer reviews improve quality and catch undiscovered issues.
4. Automated CI/CD Pipelines: Integrate security and quality checks into automated builds and deployments.
5. Dependency Scanning: Tools like Dependabot or AWS CodeGuru Reviewer analyze dependencies for security and quality issues.