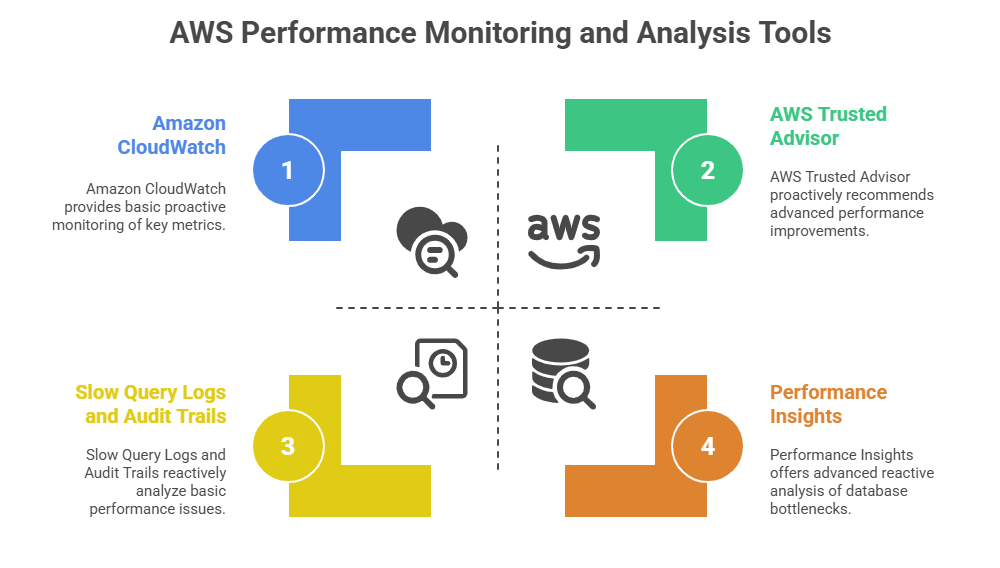
Database performance and optimization are core to ensuring efficient data storage, retrieval, and management, directly impacting application responsiveness, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Well-optimized databases deliver faster query results, handle concurrent workloads gracefully, and maintain data integrity under varying load conditions.
Achieving optimal database performance involves careful design, indexing strategies, query tuning, and resource management.
With cloud-based databases, such as those provided by AWS, additional features and services further empower developers and administrators to monitor, analyze, and optimize database workloads dynamically.
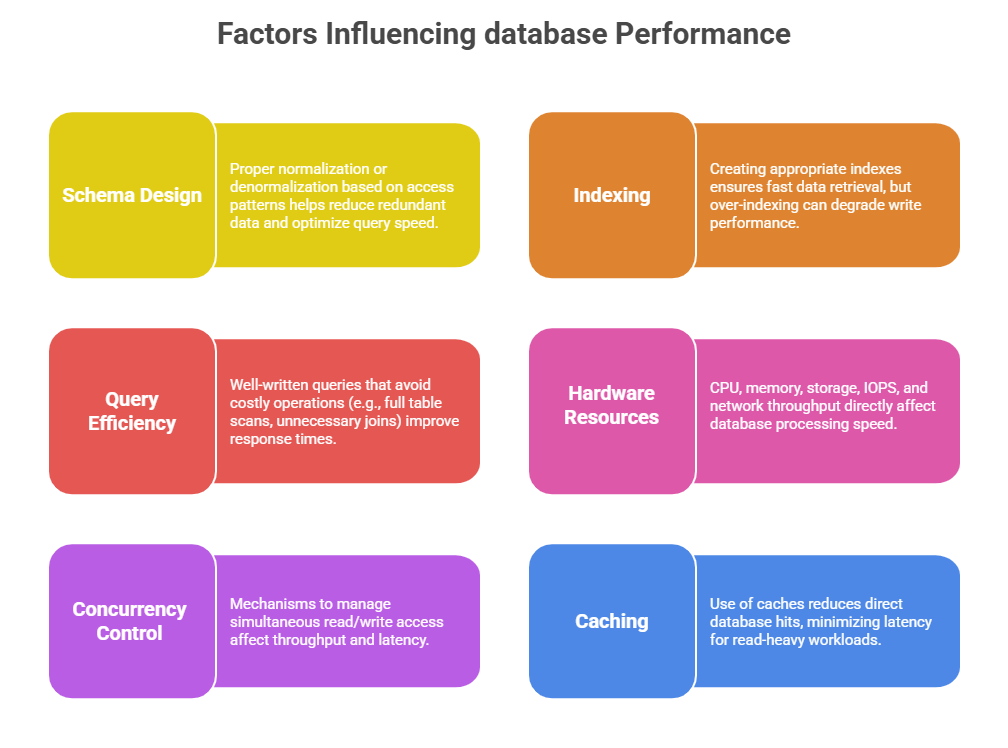
Optimization Techniques in AWS Database Services
AWS provides a variety of database services, each with specialized tools and configurations for performance tuning. The strategies listed below demonstrate how to optimize RDS, DynamoDB, and ElastiCache for different workloads.
1. Amazon RDS (Relational Databases)
Use read replicas to offload read traffic from primary instances.
Employ Multi-AZ deployments for high availability without a performance hit.
Monitor slow queries and optimize via explain plans and query tuning.
Scale compute and storage resources dynamically based on load.
2. Amazon DynamoDB (NoSQL)
Design tables and indexes based on access patterns to maximize throughput and minimize latency.
Use DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX) for in-memory caching.
Implement adaptive capacity to automatically redistribute throughput.
3. Amazon ElastiCache
Deploy Redis or Memcached caching layers to store frequently accessed data.
Optimize cache hit rates through appropriate TTL (time-to-live) and invalidation policies.
Best Practices for Database Optimization
1. Analyze application access patterns before schema and index design.
2. Regularly review and update indexes based on evolving query profiles.
3. Use parameter tuning and connection pooling for efficient resource usage.
4. Employ automated backups and maintenance tasks during low-traffic periods.
5. Leverage cloud elasticity to adjust resources proactively based on performance metrics.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.