Understanding AWS Global Infrastructure and its core services is fundamental for developing and deploying scalable, reliable, and secure applications on AWS.
The AWS infrastructure is a vast network of data centers strategically located worldwide to provide low latency, high availability, and fault tolerance.
This global infrastructure enables customers to deploy resources close to their users, comply with regional requirements, and ensure business continuity through multiple availability zones and regions.
AWS Global Infrastructure
AWS Global Infrastructure consists of the following components:
1. Regions: AWS organizes its data centers into geographic regions worldwide. Each region is a separate geographic area designed to support your applications with high availability and low latency. Customers can select one or more regions close to their end-users for optimal performance and regulatory compliance.
2. Availability Zones (AZs): Each region is further divided into multiple isolated availability zones. An AZ consists of one or more discrete data centers, each with redundant power, networking, and connectivity. Deploying applications across multiple AZs enhances fault tolerance and disaster recovery.
3. Edge Locations: These are sites deployed globally to cache copies of content closer to users for improved performance, primarily using Amazon CloudFront (AWS's Content Delivery Network). Edge locations also support other services like AWS Lambda@Edge for running code closer to users.
4. Local Zones and Wavelength Zones: AWS Local Zones place compute, storage, database, and other services closer to large population centers to support latency-sensitive applications. Wavelength Zones bring AWS services to the edge of 5G networks to support mobile and connected devices requiring ultra-low latency.
Benefits of AWS Global Infrastructure
Leveraging AWS’s vast network of regions, availability zones, and edge locations ensures business continuity, scalability, and compliance. The primary benefits are as follows:
1. High Availability and Fault Tolerance: By deploying resources across AZs and regions, AWS ensures applications can withstand infrastructure failures without downtime.
2. Low Latency: Using edge locations and choosing regions near users optimizes response times.
3. Security and Compliance: AWS regions provide data sovereignty options helping customers meet legal and compliance requirements.
4. Scalability and Flexibility: AWS infrastructure supports rapid scaling geographically based on demand.
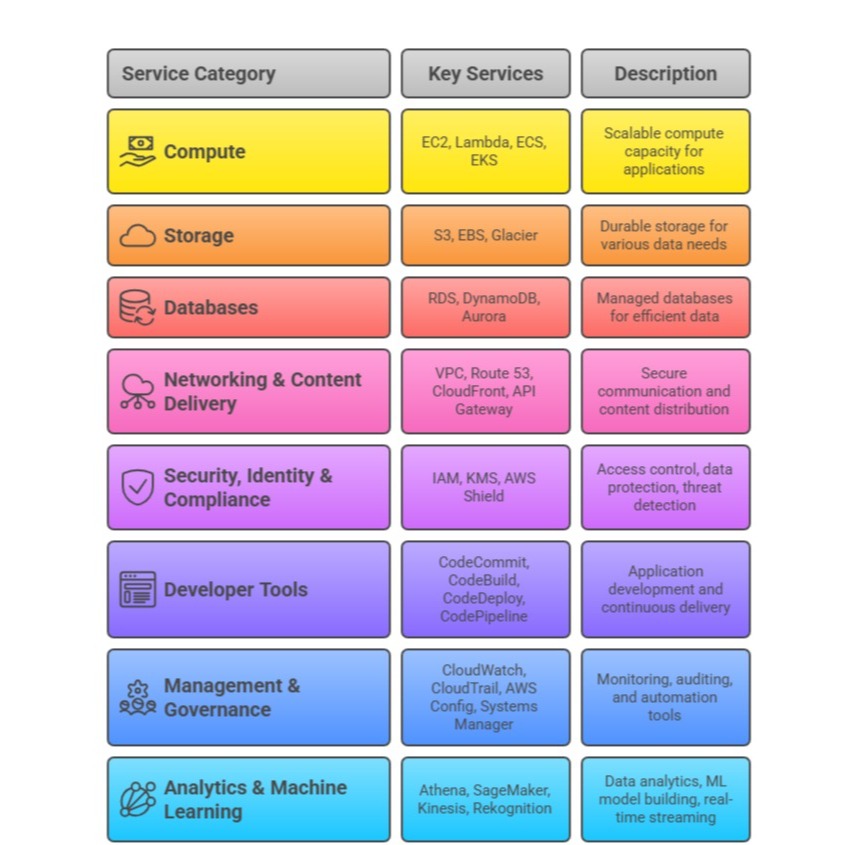
Core AWS Services Overview
AWS offers a broad portfolio of services grouped by categories essential for cloud computing solutions:
Region and AZ Selection Considerations
Choosing the right AWS region and AZ for your application depends on several factors:
1. Latency requirements: Select regions closest to your user base.
2. Cost considerations: Pricing may vary by region.
3. Compliance and data residency: Some data must reside in specific geographic locations.
4. Service availability: Not all AWS services are available in every region.
5. Disaster recovery strategy: Utilize multiple AZs or multiple regions for resiliency.
Security and Data Privacy
AWS applies stringent security controls across its global infrastructure, including physical security, network security, and operational security. Customers retain control of data and can implement additional encryption and access controls.
AWS compliance certifications and attestations cover many global standards to help customers meet regulatory requirements.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
