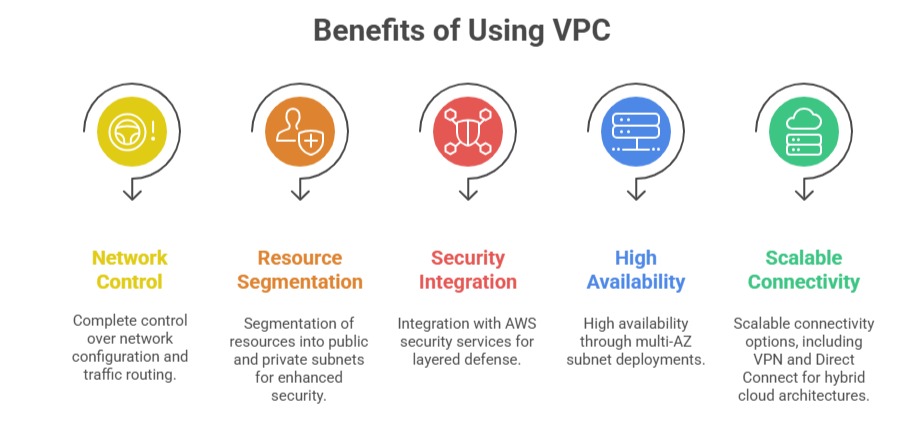
In the realm of cloud computing, network design and security are fundamental to building reliable and scalable applications. Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a core networking service that enables users to provision logically isolated virtual networks within the AWS cloud.
VPC, organizations can launch AWS resources like EC2 instances into a virtual network that they define, controlling network configuration, IP addressing, routing, and security to meet their specific requirements.
This offers the flexibility and control of a traditional on-premises network with the scalability and convenience of cloud infrastructure.
VPC Architecture and Components
At its core, a VPC provides an isolated section of the AWS cloud where users control networking features, including IP address ranges, subnets, route tables, gateways, and security settings.
1. CIDR Block (IPv4 and IPv6 Addressing): A VPC is assigned an IP address range using CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) notation, for example, 10.0.0.0/16. This defines the private IPv4 address space available within the VPC. IPv6 addressing can also be enabled for global reachability.
2. Subnets: A subnet is a segment of the VPC’s IP address range where you launch AWS resources. Subnets are categorized as public (direct internet access) or private (no direct internet access) based on routing and gateway configurations. Subnets exist in specific Availability Zones (AZs), enabling high availability.
3. Route Tables: Route tables control traffic routing within the VPC. Each subnet is associated with a route table that defines how network traffic is directed. Routes can direct internal traffic within the VPC or external traffic through gateways.
4. Internet Gateway (IGW): An IGW is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available component that allows communication between instances in the VPC and the public internet. Attaching an IGW to the VPC and configuring route tables enables public subnet internet access.
5. NAT Gateway/Instance: NAT (Network Address Translation) devices enable private subnet instances to access the internet while preventing inbound internet access. A NAT gateway is a managed AWS service that handles this traffic securely and efficiently.
6. Virtual Private Gateway (VGW): This gateway enables secure connections from the AWS VPC to a customer’s on-premises network via VPN or AWS Direct Connect.
7. Elastic IP Address: A static, publicly routable IPv4 address that can be associated with instances or NAT devices.
Security Controls in VPC
AWS VPC incorporates multiple layers of security controls that ensure robust network protection:.png)
Advanced Networking Concepts
To support large-scale and multi-tier deployments, AWS offers advanced networking capabilities that simplify connectivity and improve performance between VPCs and external networks. Essential concepts include:
1. VPC Peering: Allows private communication between two VPCs, either within the same AWS region or across regions, fostering secure and efficient sharing of resources.
2. Endpoints: These enable private connections from VPCs to supported AWS services without using public IPs or internet gateways, increasing security and reducing latency.
3. Transit Gateway: A network transit hub that connects multiple VPCs and on-premises networks, simplifying complex architectures.
4. Elastic Load Balancer (ELB): Distributes incoming traffic across multiple targets in one or more subnets to increase availability and fault tolerance.