Caching is a fundamental strategy used in modern application architectures to enhance performance, reduce latency, and improve scalability.
By temporarily storing frequently accessed data in fast, in-memory data stores, caching reduces the load on primary databases and speeds up data retrieval for end users.
Amazon Web Services offers powerful managed caching services, including Amazon ElastiCache and DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX), that simplify the implementation of caching layers while ensuring high availability and seamless integration with AWS databases.
Proper use of these caching services enables applications to operate more efficiently and deliver superior user experiences.
Amazon ElastiCache Overview
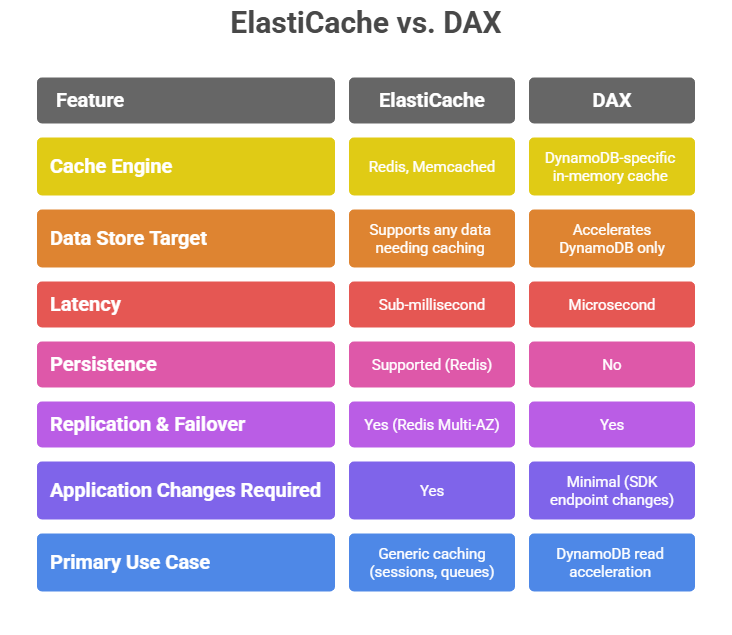
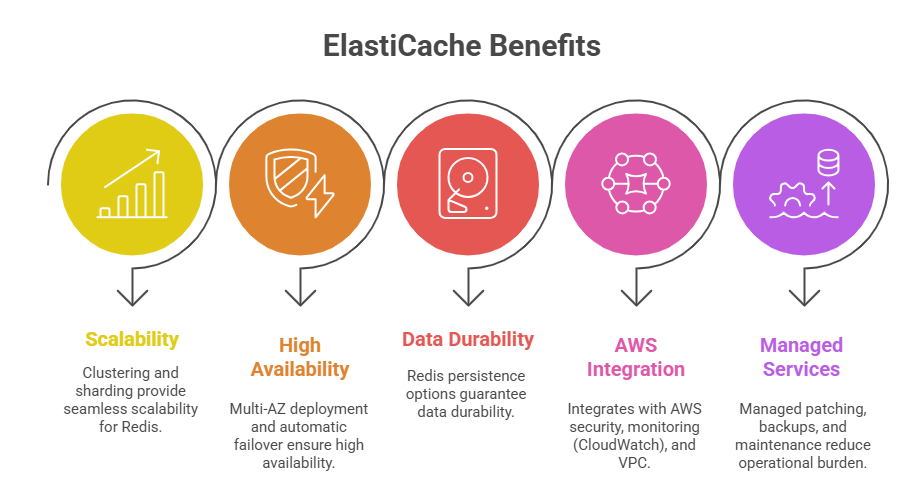
Amazon ElastiCache is a fully managed in-memory data store service that supports Redis and Memcached, two popular open-source caching engines. It is designed to provide sub-millisecond latency for read-intensive and compute-intensive workloads.
1. Use Cases: Session caching, gaming leaderboards, real-time analytics, database query results caching, and message brokering.
2. Memcached: A simple, high-performance, distributed memory object caching system. Suitable for straightforward caching use cases requiring horizontal scaling.
3. Redis: An advanced, feature-rich in-memory key-value store with support for data structures (strings, hashes, lists, sets, etc.), persistence, replication, pub/sub, transactions, and Lua scripting.
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX) Overview
DAX is an in-memory cache specifically designed for Amazon DynamoDB to accelerate read performance by caching query and scan results.
It is a fully managed, highly available service that offers microsecond latency for DynamoDB workloads without requiring application changes.
Key Features of DAX
1. Seamless Integration: DAX acts as a write-through and read-through cache between the application and DynamoDB, fully compatible with existing DynamoDB API calls.
2. Performance: Reduces time-consuming DynamoDB reads from milliseconds to microseconds.
3. Scalability and Availability: Supports clustered configurations with replication and automatic failover.
4. Code Simplicity: Does not require modifying existing application logic other than client SDK changes to include DAX endpoints.
Caching Strategies
Effective caching strategies depend on workload patterns and data characteristics. Common approaches include:
1. Write-Through Cache: Writes are simultaneously updated in cache and database, ensuring strong consistency.
2. Write-Back Cache: Writes update the cache first and then asynchronously persist to the database, which improves write performance but risks stale data upon cache failures.
3. Read-Through Cache: Reads are first attempted from the cache; on a miss, data is fetched from the database and placed in cache for future requests.
4. Cache Invalidation: Actively identifying and removing or updating stale cache entries, which is critical to maintain data consistency.
5. Time-to-Live (TTL): Configuring expiration times for cache entries to avoid indefinite caching of stale data.
Best Practices
1. Analyse application read/write patterns to select an appropriate caching strategy.
2. Use TTL judiciously to balance cache freshness and hit rates.
3. Design cache keys carefully to avoid hot partitions or key collisions.
4. Monitor cache hit/miss metrics to optimise cache performance.
5. Combine caching with database features such as read replicas for best performance.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.