AWS X-Ray is a powerful distributed tracing service designed to help developers analyze, monitor, and debug complex applications, especially those built using microservices or serverless architectures.
As modern cloud-native applications often comprise multiple interconnected services, tracing requests as they flow across these components can be challenging.
AWS X-Ray provides end-to-end visibility into the lifecycle of a request, enabling developers to pinpoint bottlenecks, diagnose errors, and optimize performance with a clear, detailed picture of application behavior.
How AWS X-Ray Works
AWS X-Ray collects trace data from applications and AWS services, assembling segments that represent units of work performed by individual components.
These segments combine to form a trace—a detailed timeline of a request’s journey through the system.
The service map visually represents interactions between services, revealing dependencies and flow, which is invaluable for understanding system architecture and troubleshooting.
Key Components
1. Segments and Subsegments: Segments represent broad components of a request, such as calls to a database or HTTP requests. Subsegments provide granular details, tracking specific operations within a segment, such as individual SQL queries or external HTTP calls.
2. X-Ray SDK and Daemon: Developers instrument their applications with AWS X-Ray SDKs for supported programming languages. The SDKs send trace data to the X-Ray daemon, which buffers and uploads data to the AWS X-Ray service efficiently.
3. Sampling: To manage volume and cost, X-Ray employs sampling algorithms that trace a configurable fraction of requests, balancing detailed insights with performance impact.
4. Annotations and Metadata: Custom data can be added to traces, aiding in filtering and analysis based on business-specific or operational parameters.
5. Service Map: An interactive graph that visualizes services and resources the application interacts with, showing latencies between nodes and highlighting errors or faults.
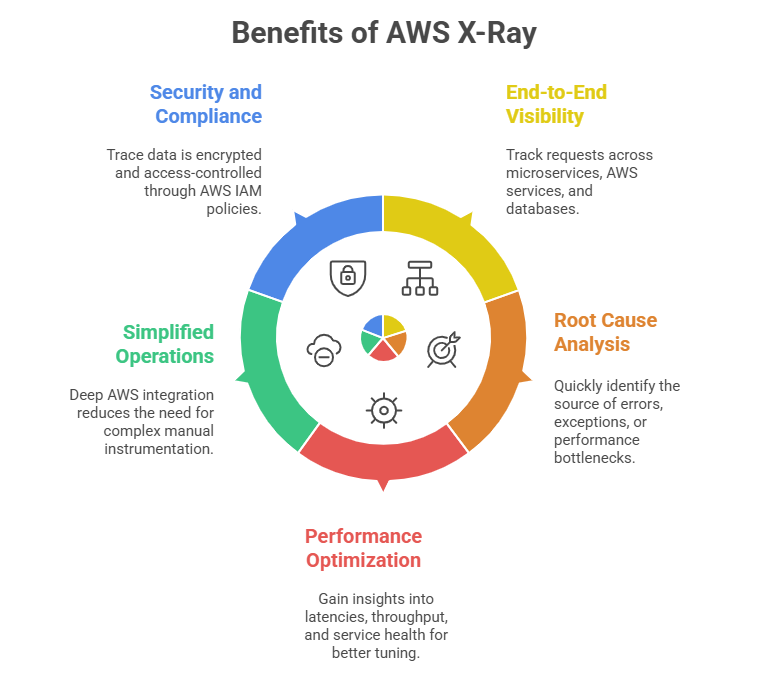
Use Cases
1. Debugging complex microservice chains to isolate issues and avoid cascading failures.
2. Monitoring serverless applications with multiple Lambda functions and API Gateway endpoints.
3. Analyzing latency contributors in user request paths to enhance customer experience.
4. Detecting and investigating service errors or slowdowns in real time.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
.png)
