Scalability and performance architecture are fundamental design principles for building cloud applications that can efficiently handle varying workloads and maintain reliable, fast response times as demand grows.
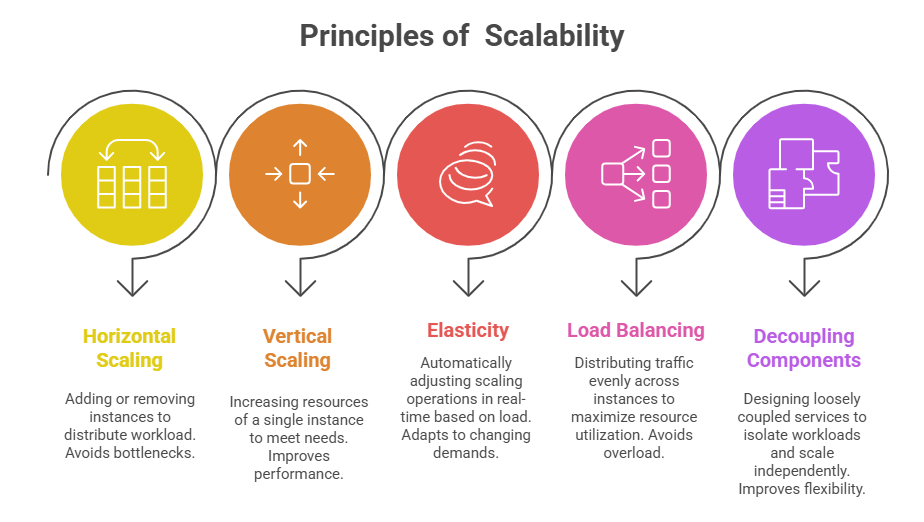
Scalability refers to the system’s ability to increase capacity to accommodate load, while performance architecture focuses on optimizing resource utilization and minimizing latency.
Together, these principles ensure that applications remain resilient and cost-effective under both typical and peak usage scenarios.
Leveraging cloud infrastructure and best practices enables engineers to architect systems that automatically adapt to changes in demand without compromising user experience or system integrity.
Performance Optimization Strategies
Improving system performance requires a combination of smart architecture, efficient data handling, and network tuning. The approaches listed below highlight essential techniques for enhancing application speed and stability.
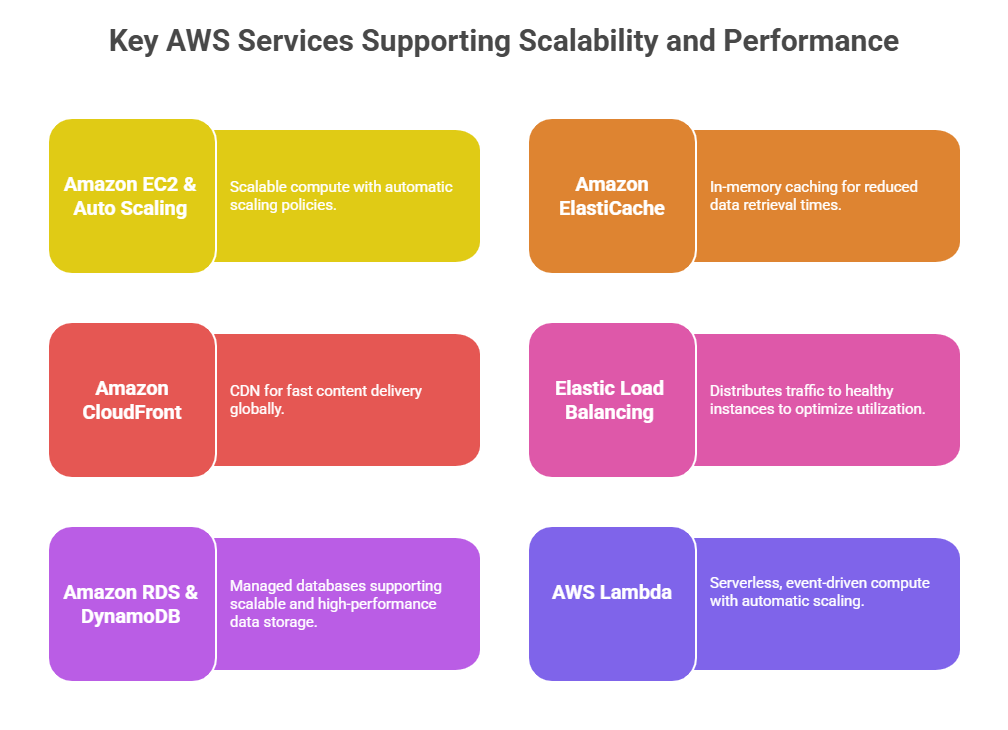
1. Caching: Implementing caches at various layers, such as in-memory caches (ElastiCache) or CDN edge caching (Amazon CloudFront), to reduce latency and backend load.
2. Efficient Database Design: Using appropriate database types (relational, NoSQL, in-memory) and indexing strategies to accelerate query performance.
3. Asynchronous Processing: Offloading long-running or non-critical tasks to background workers or queues to maintain responsiveness.
4. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Accelerate content delivery by geographically distributing assets closer to users.
5. Optimized Networking: Minimizing latency through network design, using VPC endpoints, edge locations, and efficient routing.
Design Patterns for Scalability and Performance
Building systems that scale efficiently demands modular, resilient, and data-driven design approaches. The following patterns demonstrate techniques for optimizing performance across distributed environments.
1. Event-Driven Architectures: Use event queues and messaging to enable asynchronous and decoupled processing.
2. Microservices Architecture: Isolate functionalities into independently scalable services.
3. Circuit Breaker Pattern: Prevent cascading failures and allow graceful degradation under high load.
4. Database Sharding and Partitioning: Split large datasets for parallel access and faster querying.
5. Caching Layers: Employ multi-tier caching strategies to reduce database load and latency.
.png)