Infrastructure as Code (IaC) represents a transformative approach in the management and provisioning of cloud infrastructure by using code and automation instead of manual processes.
This approach enables organizations to define, deploy, and maintain their infrastructure reliably and repeatedly through declarative configurations.
AWS CloudFormation is one of the foremost IaC services designed to help users model and provision AWS resources predictably and efficiently.
By managing infrastructure through templates, CloudFormation promotes automation, consistency, and version control, reducing errors and operational overhead.
What is Infrastructure as Code?
Infrastructure as Code involves writing scripts or templates that describe the desired state of infrastructure components—such as compute instances, storage resources, networking configurations, and security settings.
Instead of manually creating or configuring resources, these code files are executed by IaC platforms to provision and configure infrastructure automatically.
IaC supports automation, repeatability, scalability, and alignment with development practices like version control and code reviews.
AWS CloudFormation Overview
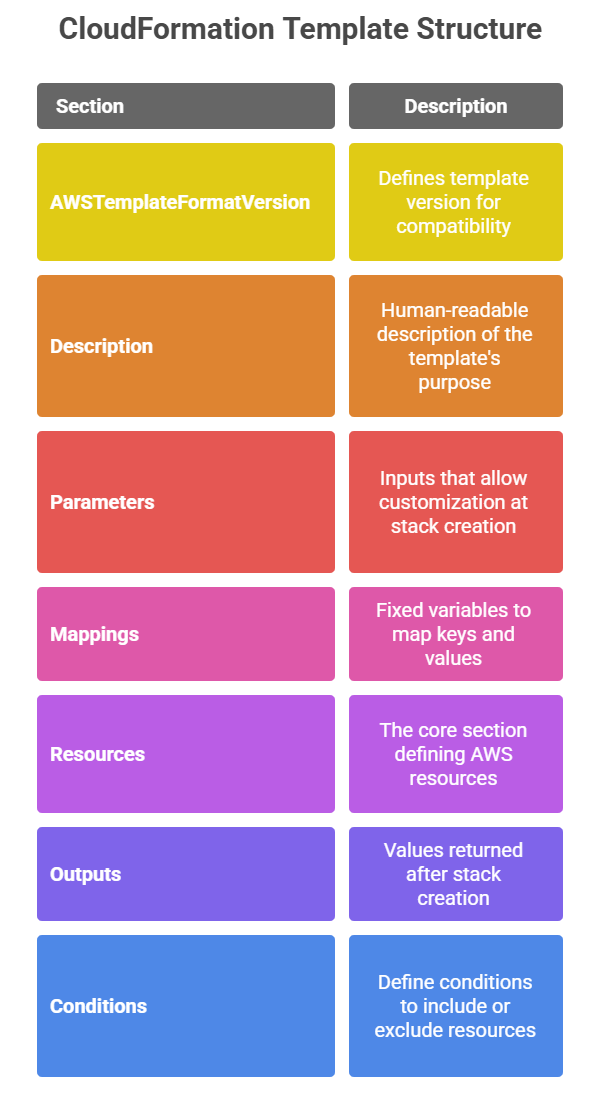
CloudFormation enables the definition and deployment of AWS infrastructure using JSON or YAML templates. These templates specify a collection of related resources, their configurations, dependencies, and runtime parameters.
Key Features of AWS CloudFormation:
1. Declarative Templates: Users declare 'what' resources are needed, not 'how' to create them, simplifying infrastructure management.
2. Stack Management: Resources defined in a template are managed as stacks, enabling easy creation, update, and deletion.
3. Resource Dependencies: Automatically figures out dependencies and provisioning order for complex infrastructure setups.
4. Change Sets: Preview proposed changes before applying them to existing stacks to avoid disruptions.
5. Drift Detection: Monitors stack resources for configuration changes made outside CloudFormation and alerts users.
6. Stack Policies: Protect sensitive or critical resources from accidental updates during stack modifications.
Common Use Cases
1. Consistent multi-environment deployments (development, testing, production).
2. Automated provisioning of complex applications with interconnected AWS resources.
3. Infrastructure versioning and rollback to known states.
4. Integration with CI/CD pipelines for continuous deployment.
5. Disaster recovery by recreating environments rapidly.
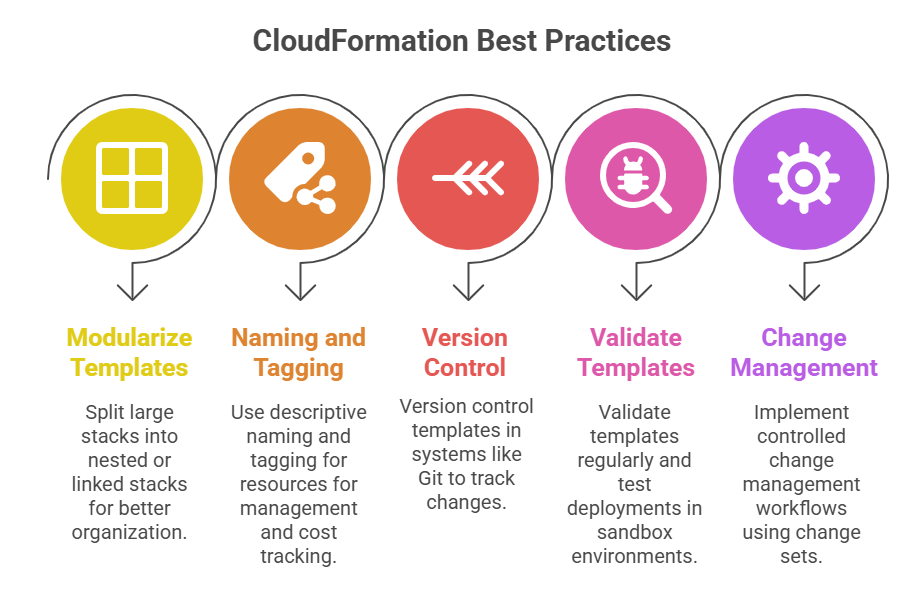
Advantages of CloudFormation and IaC
Adopting IaC with CloudFormation brings structure, transparency, and repeatability to cloud deployments. Here are the core benefits that demonstrate its value in secure and efficient cloud management:
1. Speed and Efficiency: Automated, repeatable deployments accelerate development and deployment cycles.
2. Consistency and Standardization: Avoid errors and configuration drift by enforcing standardized setups.
3. Traceability and Auditing: Infrastructure changes are version-controlled and auditable using source control systems.
4. Cost Control: Easily spin up and tear down test environments, reducing costs.
5. Integration with AWS Ecosystem: Supports nearly all AWS resources, works with CloudTrail, IAM, and third-party tools.