Network and application security form the foundation of protecting cloud environments, data, and digital services from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and operational disruptions.
In cloud architectures, securing the network perimeter and application layers ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of resources.
AWS provides a comprehensive suite of tools and best practices to design resilient, secure network architectures alongside robust application defence mechanisms.
These combined measures help shield workloads from evolving threats while maintaining compliance with industry standards.
Network Security in AWS
Network security encompasses controls designed to protect data as it travels across network boundaries and restrict unauthorized entry points.
Key Components:
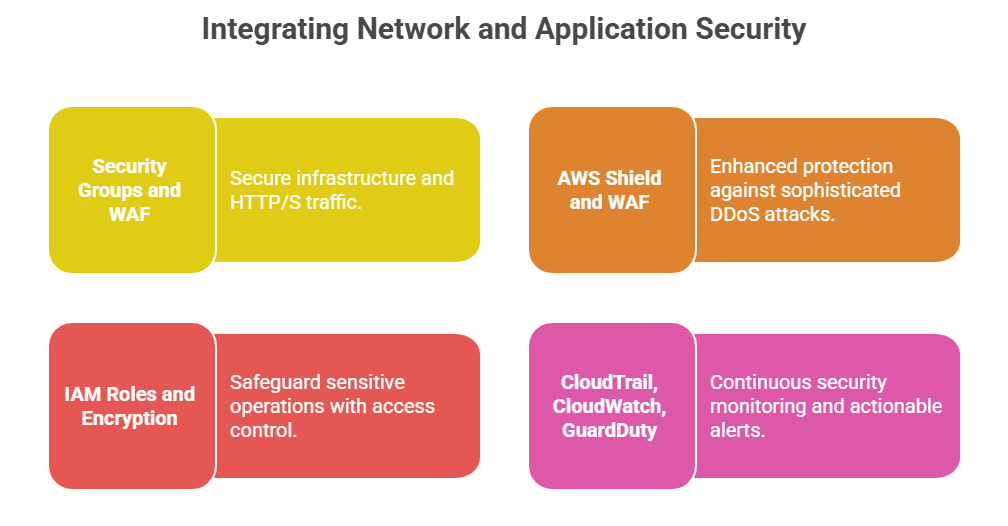
1. Security Groups: Function as virtual stateful firewalls attached to Amazon EC2 instances (or other resources), controlling inbound and outbound traffic at the instance level. Rules can be defined by IP, protocol, and port.
2. Network Access Control Lists (NACLs): Stateless firewalls applied at the subnet level within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). NACLs evaluate incoming and outgoing traffic separately based on allow or deny rules.
3. Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Provides logically isolated virtual networks where users define IP address ranges, subnets, route tables, and gateways, creating secure networking boundaries.
4. VPC Peering and Transit Gateways: Enable secure private connectivity between VPCs within or across AWS accounts and simplify complex network topologies, enhancing secure communication.
5. AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF): Protects web applications by filtering malicious traffic and blocking common web exploits such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
6. AWS Shield: Provides managed Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection for applications running on AWS, offering Standard and Advanced tiers for different security needs.
7. Traffic Inspection and Logging: VPC Flow Logs capture IP traffic data for monitoring and in-depth security analysis.
Application Security in AWS
Securing applications extends beyond network controls to include safeguarding application logic, data, and authentication mechanisms.
Key Components:
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controls granular permissions to access AWS resources, enforcing the principle of least privilege.
2. Encryption: Data must be encrypted at rest and in transit using AWS services like AWS KMS and TLS protocols to guard against data breaches.
3. Amazon Cognito: Provides user authentication, authorization, and user management, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) for web and mobile applications.
4. Security Best Practices:
Regularly update and patch application dependencies and runtime environments.
Conduct code scans and vulnerability assessments for common security flaws.
Enforce secure coding practices and input validation to prevent injection attacks.
Implement logging and monitoring to detect security incidents promptly.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
