Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a foundational service within Amazon Web Services that delivers scalable and resizable compute capacity in the cloud.
EC2 allows individuals and organizations to quickly provision virtual servers, known as instances, to host applications and services without the upfront cost and delay of purchasing physical hardware.
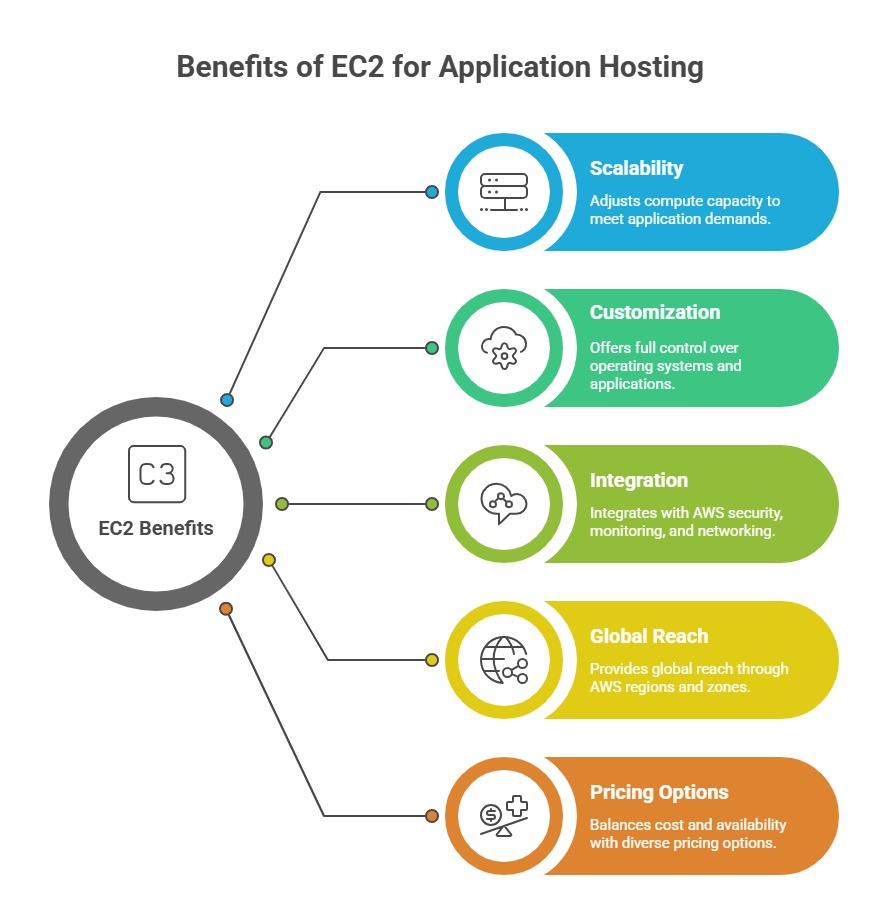
This flexibility enables dynamic scaling to meet changing workloads while maintaining full control over instance configurations, operating systems, and installed software.
Leveraging EC2 is crucial for hosting applications that require reliable, secure, and performant infrastructure in the cloud.
EC2 Architecture and Features
Amazon EC2 offers a wide range of instance types optimized for different use cases, enabling users to select compute, memory, storage, and networking configurations best suited for their applications.
1. Instance Types and Families: EC2 instances are grouped based on their optimized capabilities, including:
General Purpose (balance of compute, memory, network)
Compute Optimized (high CPU power for batch processing, gaming)
Memory Optimized (large memory for databases, caches)
Storage Optimized (high throughput for large datasets)
GPU Instances (for machine learning, graphics processing)
2. Instance Lifecycle: Users can launch, stop, start, reboot, and terminate EC2 instances on demand, providing flexibility and cost control.
3. Amazon Machine Images (AMIs): AMIs are pre-configured templates containing operating system and software configurations used to launch instances quickly and consistently.
4. Elastic Block Store (EBS): Persistent block storage volumes that can be attached to instances; data remains intact even when instances are stopped or terminated.
5. Elastic IP Addresses: Static public IP addresses that can be dynamically associated with instances to enable consistent external connectivity.
6. Security Groups: EC2 instances are protected by security groups acting as virtual firewalls, controlling inbound and outbound traffic at the instance level.
Application Hosting Using EC2
EC2 provides a highly customizable environment for hosting a variety of applications, from simple websites to complex enterprise-grade systems.
1. Web Hosting: Deploy simple web servers using Apache, Nginx, or Microsoft IIS to serve static or dynamic content.
2. Application Servers: Host backend logic and APIs, interacting with databases and other services.
3. Containers and Orchestration: While EC2 can run containerized workloads, it can integrate with Amazon ECS and EKS for managed container orchestration.
4. Autoscaling: EC2 instances can be grouped in Auto Scaling groups to automatically add or remove instances based on defined metrics, ensuring applications remain available and performant.
5. Load Balancing: Elastic Load Balancers (Application, Network, or Classic) distribute incoming network traffic across multiple EC2 instances to maintain fault tolerance and improve responsiveness.
Cost Optimization and Performance Monitoring
Users can optimize costs with EC2 in several ways:
| Cost Optimization Method | Description | Ideal Use Case | ||
| On-Demand Instances | Flexible pay-as-you-go pricing model where you pay only for the compute time used. | Best for short-term or unpredictable workloads that cannot be interrupted. | ||
| Reserved Instances | Offer up to 75% discount compared to On-Demand pricing by committing to a one-year or three-year term. | Suitable for steady-state workloads with predictable usage. | ||
| Spot Instances | Allow users to bid for unused AWS capacity at discounted rates, often up to 90% off. | Ideal for fault-tolerant, flexible workloads that can handle interruptions (e.g., big data or testing). |
Performance can be tracked using Amazon CloudWatch, providing metrics such as CPU utilization, disk I/O, and network traffic to monitor health and optimize resource usage.