Encryption and key management are critical components of data security, ensuring that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access both at rest and during transmission.
Encryption converts readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) that can only be deciphered by authorized parties holding the correct cryptographic keys.
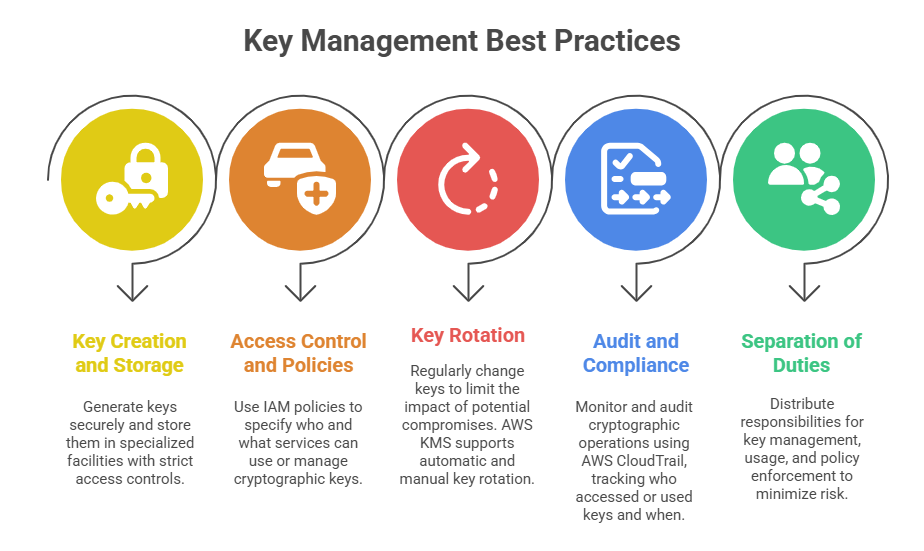
Effective key management involves the creation, storage, rotation, and control of these cryptographic keys, which underpins the overall strength and reliability of encryption strategies.
AWS provides comprehensive services and tools, such as AWS Key Management Service (KMS) and AWS CloudHSM, that simplify implementing robust encryption and key management across cloud workloads.
Data Encryption Fundamentals
Encryption safeguards data confidentiality by transforming data through cryptographic algorithms. Common encryption types include:
1. Encryption at Rest: Protects stored data on disks, databases, or object storage by encrypting it using strong algorithms. This prevents data exposure in case of unauthorised physical or logical access.
2. Encryption in Transit: Encrypts data as it moves between clients, servers, and across networks using protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS), preventing interception or tampering during transmission.
AWS Encryption and Key Management Services Overview
AWS provides scalable, secure, and integrated encryption services that support a variety of use cases:
1. AWS Key Management Service (KMS): A fully managed service for creating, controlling, and auditing cryptographic keys. AWS KMS simplifies encryption by centrally managing keys and enforcing access policies while offering integration with most AWS services.
2. AWS CloudHSM: A dedicated hardware security module (HSM) service for customers requiring single-tenant key storage with direct control over key lifecycle and compliance adherence.
3. Encryption SDKs: Developer libraries enabling client-side encryption and integrated encryption in applications.
4. Server-Side Encryption (SSE): AWS services offer built-in server-side encryption options where data is automatically encrypted/decrypted by AWS using KMS-managed keys (SSE-KMS), service-managed keys (SSE-S3), or customer-provided keys (SSE-C).
Encryption Use Cases in AWS
Below are the major scenarios where encryption is commonly applied:
1. Protecting Data at Rest: Encrypt databases, file systems, and object storage (Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, Amazon RDS).
2. Securing Data in Transit: TLS encryption for API endpoints, web traffic, and communications between services.
3. Client-Side Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data before sending it to the cloud to maintain control over encryption keys outside AWS.
4. Digital Signing and Verification: Use asymmetric keys for signing data and detecting unauthorized modification.
5. Multi-Tenant Isolation: Use keys and cryptographic boundaries to safely isolate data between customers or services.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.