AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service that lets developers run code without provisioning or managing servers.
While Lambda abstracts much of the infrastructure, optimizing function performance is critical to reduce latency, manage costs, and deliver responsive applications.
Performance optimization in AWS Lambda involves fine-tuning resource allocation, minimizing cold starts, and adopting coding best practices to ensure efficient execution.
Thoughtful optimization improves user experience, lowers operational expenses, and scales seamlessly with demand.
Strategies to Optimize AWS Lambda Performance
To maximize the efficiency of AWS Lambda functions, it’s essential to optimize resources, code, and networking configurations. Below are key strategies to ensure faster execution and smoother scaling.
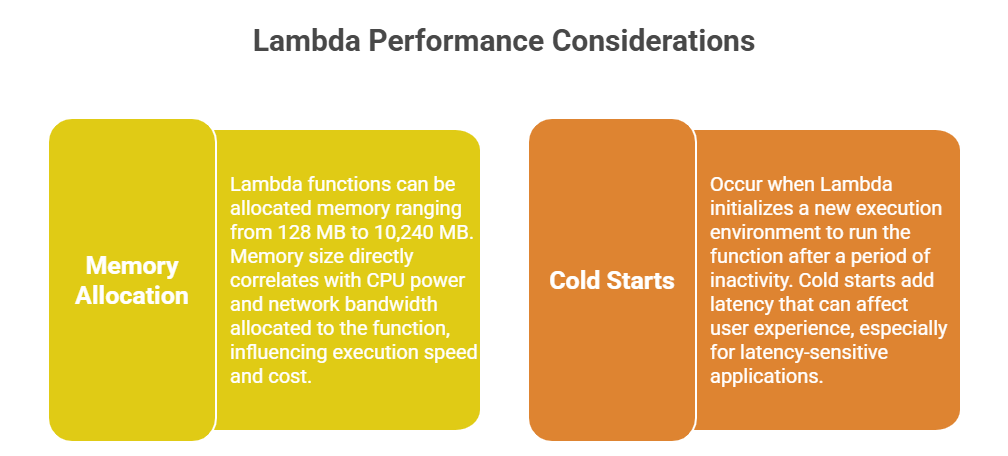
1. Right-Sizing Memory Configuration
Allocate sufficient memory to balance performance and cost.
Use the AWS Lambda Power Tuning tool to empirically identify optimal memory settings.
2. Minimize Cold Start Impact
Keep functions warm by scheduling periodic invocations.
Use Provisioned Concurrency to pre-allocate execution environments with minimal initialization delay.
3. Reduce Deployment Package Size
Minimize the Lambda package size to speed up deployment and initialization.
Share common libraries using Lambda Layers.
4. Optimize Code Execution
Adopt efficient algorithms and avoid unnecessary dependencies.
Reuse database connections or client instances outside the handler function to leverage container reuse.
Utilize asynchronous programming where appropriate.
5. Leverage VPC Optimization
Avoid unnecessary VPC configurations unless required, as VPC-enabled functions have higher cold start latency.
Use AWS VPC features like AWS PrivateLink and NAT gateways to optimize network routing.
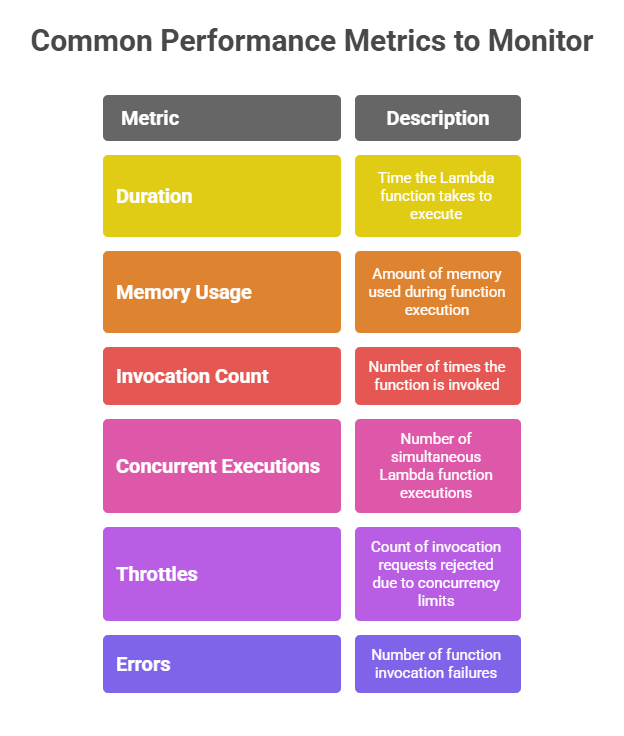
6. Monitoring and Profiling
Use AWS CloudWatch logs and AWS X-Ray tracing to identify bottlenecks and latency distributions.
Analyze invocation durations and error rates regularly and adjust optimizations accordingly.
Best Practices
1. Profile and benchmark functions regularly to detect regressions.
2. Use environment variables for configuration to keep code clean and maintainable.
3. Implement retries and exponential backoff in downstream calls to improve resilience.
4. Employ AWS Lambda Extensions to enhance monitoring and security without impacting performance.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.