In today’s digital landscape, safeguarding secrets and sensitive data is crucial to maintaining application security and compliance.
Secrets such as API keys, passwords, database credentials, tokens, or private certificates provide privileged access to critical systems and data.
Improper handling or exposure of secrets can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and potentially serious operational and reputational damages.
AWS offers specialized services and best practices designed to securely store, manage, rotate, and control access to secrets, empowering organizations to maintain confidentiality and secure integrations in their cloud applications.
Understanding Secrets and Sensitive Data
Secrets encompass any sensitive strings or binary data that grant access to systems or data. These include:
1. Database connection credentials
2. API keys and access tokens
3. Encryption keys and certificates
4. OAuth and authentication tokens
5. Sensitive configuration parameters
Challenges in Secrets Management
Hard-coding secrets in application source code or configuration files increases exposure risk and complicates secret rotation. Enterprises must balance operational agility with stringent security controls while enforcing minimal exposure and clear auditability.
AWS Secrets Management Solutions
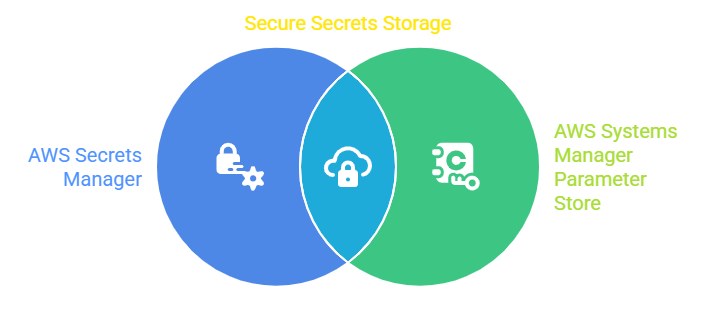
1. AWS Secrets Manager: A fully managed service that secures secrets by encrypting them, automatically rotating credentials, and controlling access through fine-grained IAM policies. It integrates seamlessly with many AWS and third-party services, triggering rotation workflows using Lambda functions without requiring application downtime.
2. AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store: Provides a centralized, secure storage for configuration data and secrets. It supports encrypted parameters and integrates with IAM for access control. Best suited for simpler secrets management with optional version tracking and notifications.
Security Features and Best Practices
AWS offers built-in tools and best practices to ensure sensitive data is securely managed across services. Below are the key security features and techniques that strengthen protection and maintain compliance:
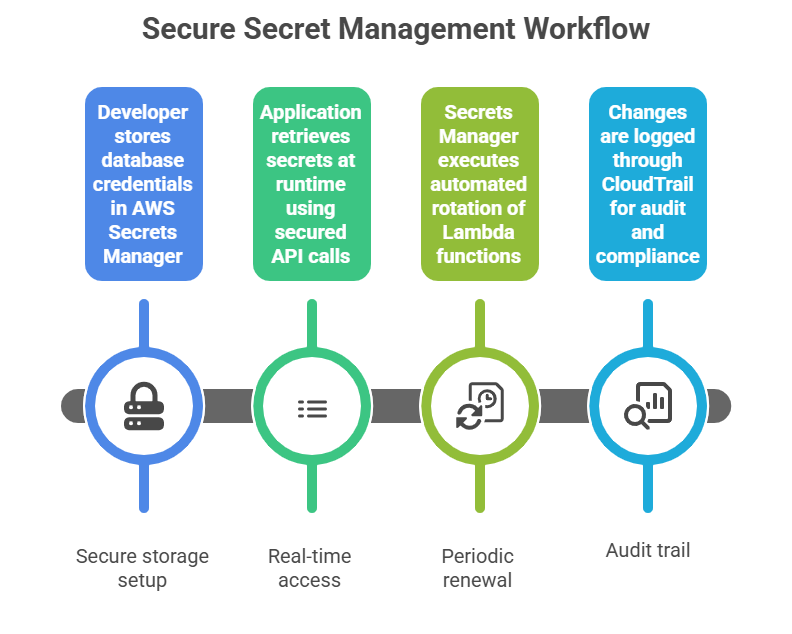
1. Encryption at Rest and In Transit: Both Secrets Manager and Parameter Store encrypt data with AWS Key Management Service (KMS) by default, ensuring data confidentiality.
2. Fine-Grained Access Control: Use IAM policies to restrict who or what services can retrieve or modify secrets.
3. Automatic Secret Rotation: Set up Lambda-based rotation to periodically refresh credentials without manual intervention.
4. Auditing and Monitoring: Use AWS CloudTrail to log all secret access and management activities, providing accountability and detecting anomalies.
5. Integration with Applications: Secrets retrieval APIs allow runtime fetching of secrets, eliminating the need to embed secrets in code or environment variables.