Compliance frameworks establish mandatory requirements to protect sensitive data, maintain privacy, and ensure information security across various industries. Linux systems, commonly used for hosting critical applications and storing sensitive information, must adhere to these regulatory standards.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is a security framework designed to protect cardholder data across payment processing systems. It applies to all organizations that store, process, or transmit credit card information and requires the implementation of strict security controls to reduce the risk of data breaches.
Linux systems are commonly used as transaction servers in such environments and therefore must be securely hardened and extensively logged to meet PCI DSS requirements.
Key security requirements under PCI DSS include:
1. Secure network architecture and proper firewall configuration
2. Strong authentication mechanisms and strict access control
3. Encryption of cardholder data both in transit and at rest
4. Continuous monitoring, vulnerability management, and regular auditing
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is a European Union regulation aimed at protecting personal data and ensuring the privacy of individuals. It applies to any organization that processes the personal data of EU residents, regardless of where the organization is located.
To comply with GDPR, systems handling personal data must be designed with strong security, accountability, and transparency in mind, including properly secured Linux servers.
.png)
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is a U.S. regulation designed to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of Protected Health Information (PHI). It applies to healthcare providers, health insurers, and their associated business entities that handle sensitive medical data.
Compliance requires the implementation of strong administrative, physical, and technical safeguards, particularly on systems such as Linux-based healthcare platforms.
Key HIPAA security requirements include:
1. Access controls that limit exposure of PHI to authorized users only
2. Audit controls to record and monitor system activities involving health data
3. Integrity controls to ensure PHI is not altered or destroyed improperly
4. Encryption and secure transmission mechanisms for protecting health data
Linux-based health systems must therefore enforce strict access management, perform regular integrity checks, and use encrypted communication channels to meet HIPAA compliance requirements.
Common Linux Security Practices Across Frameworks
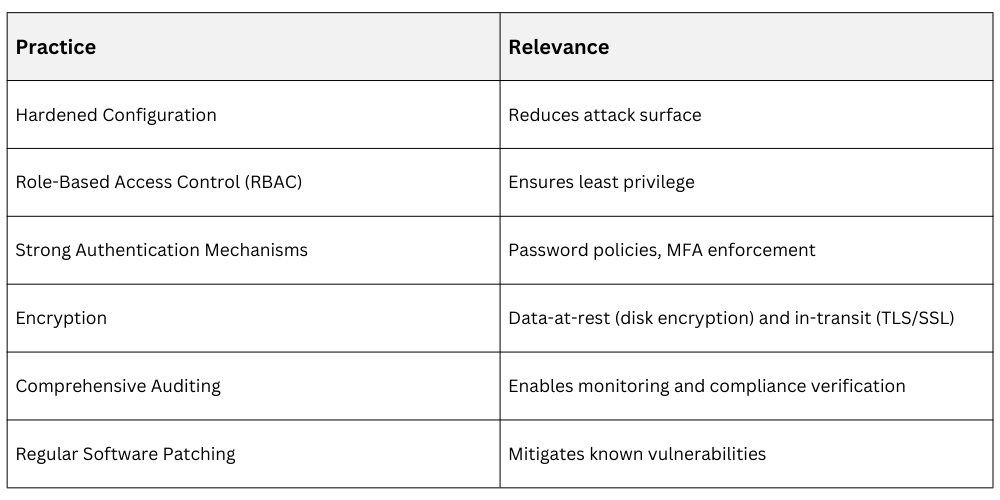 Linux Tools Supporting Compliance
Linux Tools Supporting Compliance
1. Auditd: Kernel-level auditing framework for logging system access.
2. SELinux/AppArmor: Mandatory Access Controls for application confinement.
3. Encryption Utilities: OpenSSL, LUKS disk encryption for data protection.
4. Configuration Management: Tools like Ansible or Puppet to enforce consistent security configurations.
