Transparent communication is a foundational practice for building credibility and trust within organisations and with external stakeholders. It entails openly sharing information, fostering honest dialogue, and ensuring clarity and accessibility of messages.
In today’s interconnected and fast-paced business environment, transparency is not optional but essential for sustaining productive relationships, enhancing employee engagement, and driving better decision-making.
Credibility earned through transparent communication paves the way for stronger collaboration, reduced uncertainty, and an organisational culture anchored in respect and accountability.
Why Transparency Builds Trust
Sharing information candidly helps reduce uncertainty, encourage participation, and reinforce reliability. Presented below is a list of ways transparency directly contributes to stronger, trust-based relationships.
1. Openness Creates Confidence: Sharing unvarnished information, including challenges and setbacks, signals integrity and honesty.
2. Reduces Uncertainty and Rumours: Timely dissemination prevents misinformation and builds a stable, predictable environment.
3. Engages Stakeholders Actively: Transparent dialogue invites feedback, questions, and collective problem-solving.
4. Demonstrates Accountability: Ownership of both successes and mistakes fosters respect and credibility.
5. Aligns Actions with Words: Consistent, truthful communication reinforces reliability and authenticity.
Key Principles of Transparent Communication
Communicating with openness fosters credibility and engagement when done thoughtfully and systematically. Highlighted below are the principles that form the foundation of transparent communication.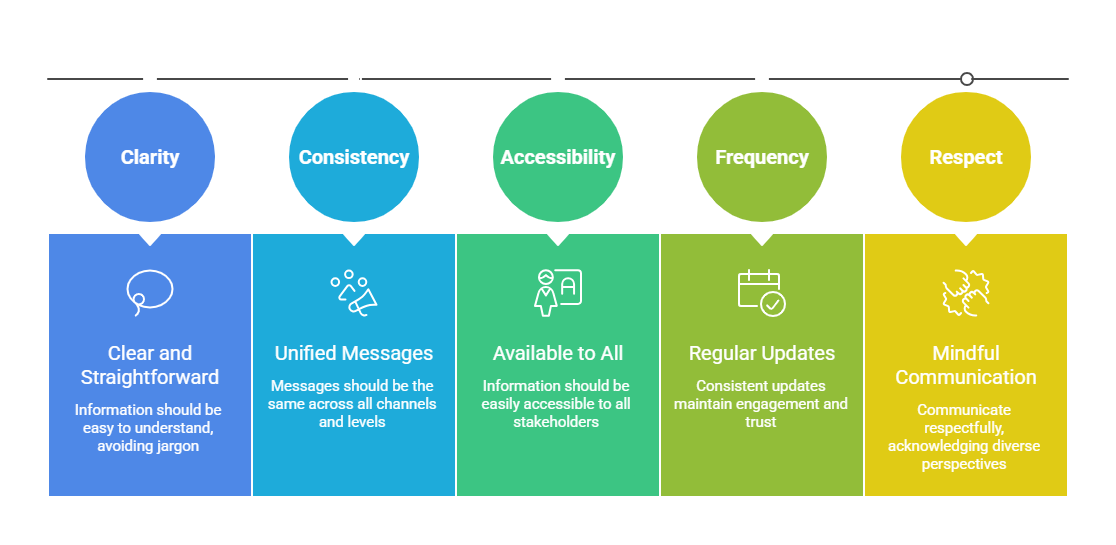
Practical Strategies to Foster Transparency
Creating a transparent culture involves consistent communication, honesty, and recognition of both successes and obstacles. The following approaches can help implement transparency effectively across teams.
1. Promote Open Dialogue: Encourage questions, ideas, and concerns. Use town halls, team meetings, and digital collaboration tools.
2. Overcommunicate Where Necessary: Don’t assume knowledge; provide comprehensive updates, especially during changes or crises.
3. Use Clear Visuals and Data: Present evidence visually to support claims and enhance comprehension.
4. Acknowledge Challenges Promptly: Address problems and corrective actions honestly before they escalate.
5. Share Decision-Making Rationale: Explain why decisions were made, including trade-offs considered.
6. Celebrate Wins Transparently: Share successes with credit to contributors, reinforcing positive culture.
Benefits of Transparent Communication
Clarity and openness in communication lead to stronger trust and organisational cohesion. Some of the benefits are improved collaboration, employee retention, smoother change processes, and a credible public image.
1. Builds Long-Term Trust: Stakeholders develop confidence in leadership and processes.
2. Strengthens Collaboration: Open environments foster teamwork and innovation.
3. Improves Morale and Retention: Employees who understand and trust leadership are more engaged.
4. Facilitates Change Management: Transparency smooths transitions and reduces resistance.
5. Enhances Reputation: Credible brands attract customers, partners, and talent.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.