Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) is a foundational step in the data analysis process, designed to help analysts understand the underlying structure and main characteristics of a dataset.
It involves using statistical and graphical techniques to uncover patterns, detect anomalies, and test assumptions without predetermined hypotheses.
It provides an open-ended, iterative approach that enables data scientists and stakeholders to grasp the data’s complexities, validate its quality, and prepare it for more sophisticated modeling or decision-making.
This stage ensures that subsequent analyses are based on reliable, well-understood data, ultimately leading to accurate and actionable insights.
Purpose of Exploratory Data Analysis
The purpose of EDA encompasses several key objectives necessary for robust data understanding and analysis readiness:
1. Data Familiarization: Gain a deep understanding of the dataset’s features, including the types of variables, distributions, and range of values.
2. Detecting Data Quality Issues: Identify missing values, outliers, and errors that might compromise analysis results.
3. Uncovering Patterns and Relationships: Visualize and analyze relationships between variables, including correlations, clusters, or trends that can inform hypotheses.
4. Validating Assumptions: Check if the data meet the assumptions required for applying specific statistical methods or models.
5. Hypothesis Generation: Formulate new questions or potential explanations based on observed data patterns.
6. Guiding Modeling Decisions: Inform the choice of appropriate modeling techniques and feature engineering based on data characteristics.
Importance of Exploratory Data Analysis
EDA’s significance extends beyond preliminary investigation; it fundamentally shapes the quality and credibility of data-driven outcomes.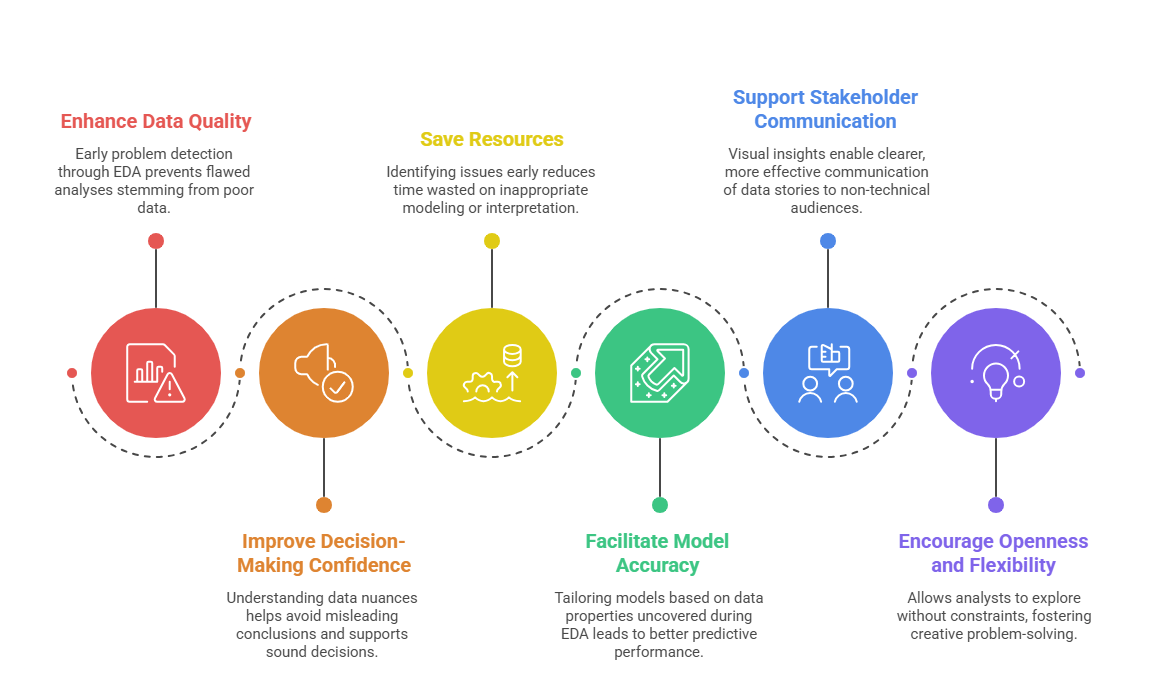
Common EDA Techniques and Tools
EDA utilizes a variety of descriptive statistics and visualization tools, including:
1. Univariate Analysis: Analysis of individual variables using histograms, box plots, and summary statistics to understand distribution and central tendency.
2. Bivariate and Multivariate Analysis: Exploring relationships with scatter plots, correlation matrices, cross-tabulations, and pair plots.
3. Outlier Detection: Identifying extreme values and anomalies through box plots and statistical tests.
4. Missing Value Analysis: Quantifying and visualizing gaps in data.
Popular tools to perform EDA include Python (Pandas, Matplotlib, Seaborn), R (ggplot2, dplyr), Tableau, and Power BI.
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.