Data validation and quality monitoring are integral components of maintaining high-quality data essential for effective analytics and decision-making.
It is the process of ensuring that data entered into systems is accurate, complete, and meets predefined criteria before being used.
Quality monitoring involves ongoing oversight and measurement of data quality to detect issues promptly and maintain data integrity over time.
Together, these practices safeguard against errors, inconsistencies, and degradation of data, enabling organizations to rely confidently on their data assets.
Understanding Data Validation
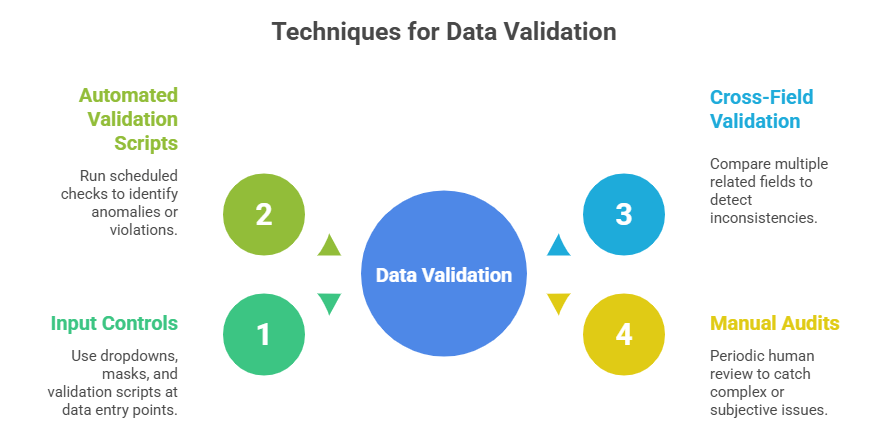
Data validation is the set of rules and procedures applied to incoming data to check for correctness, completeness, and compliance with expected standards. It can occur at the point of data entry, during data integration, or before analysis.
Key Aspects of Data Validation
1. Syntax Validation: Checks that data conforms to the prescribed format (e.g., date formats, numerical ranges).
2. Semantic Validation: Ensures data makes logical sense (e.g., a birth date is not in the future).
3. Uniqueness Checks: Prevents duplicate records, ensuring each entity is uniquely represented.
4. Referential Integrity: Ensures relationships between data elements are consistent (e.g., foreign keys match primary keys).
5. Business Rules Enforcement: Verifies data aligns with organizational policies and domain-specific constraints.
Quality Monitoring: Sustaining Data Integrity
Data quality monitoring involves continuous evaluation to ensure data remains accurate, complete, and reliable over its lifecycle. It helps organizations proactively address data quality issues before they impact analysis or operations.
Components of Quality Monitoring
1. Data Quality Metrics: Define and measure indicators such as completeness, accuracy, consistency, timeliness, and validity.
2. Dashboards and Alerts: Visual tools and automated notifications to track data quality trends and flag deviations.
3. Root Cause Analysis: Investigate recurring issues to identify systemic problems or process gaps.
4. Data Stewardship and Governance: Assign responsibility for data quality oversight and enforcement of standards.
5. Feedback Loops: Use monitoring outcomes to improve data collection and validation procedures continuously.
Monitoring Techniques
1. Sampling and Profiling: Regularly assess samples to detect irregularities in large datasets.
2. Trend Analysis: Track historical data quality to predict potential future issues.
3. Anomaly Detection: Use statistical or machine learning methods to spot unusual patterns indicative of data errors.
Best Practices for Effective Validation and Monitoring
As data complexity grows, consistent validation and structured monitoring become indispensable. The following recommendations provide guidance for enhancing these capabilities.
1. Incorporate validation early in the data lifecycle to prevent propagation of errors.
2. Leverage automation to handle large volumes and maintain consistency.
3. Collaborate across departments for holistic governance and issue resolution.
4. Maintain comprehensive documentation and standards for validation and quality.
5. Continuously train data users and custodians on responsibilities and tools.