APT (Advanced Package Tool) is a powerful and user-friendly command-line package management system widely used in Debian-based Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and Kali Linux.
It automates the process of installing, updating, and managing software packages from online repositories, ensuring users can access the latest, most secure, and compatible versions with ease.
Updating Package Information with apt update
Before installing or upgrading software, it is essential to synchronize local package databases with the latest information from software repositories. This ensures your system knows about all available updates and new packages.
Basic command:
sudo apt updateWhen executed, APT fetches the latest package lists from the URLs configured in /etc/apt/sources.list and other source files. This command does not upgrade any installed packages; it only refreshes metadata such as package versions and dependencies.
Output includes a summary of packages that can be upgraded.
Upgrading Installed Packages with apt upgrade
After updating package lists, apt upgrade installs the newest versions of all currently installed packages without removing anything.
Command:
sudo apt upgradeapt upgrade compares currently installed package versions with those available in updated repositories and prompts for confirmation before proceeding. It only upgrades packages that can be updated without uninstalling or adding new dependencies.
To upgrade a specific package:
sudo apt upgrade package_nameUse the -y flag for automatic yes to prompts:
sudo apt upgrade -yFull System Upgrade with apt full-upgrade
The full-upgrade command is more aggressive and can remove or install packages to resolve complex dependency changes.
Command:
sudo apt full-upgradeUseful for major system upgrades, such as between distribution releases. It should be used with caution as it may uninstall packages.
Installing New Software with apt install
To install new packages, use:
sudo apt install package_nameAPT automatically resolves dependencies and prompts for confirmation before downloading and installing packages.
Example:
sudo apt install firefoxTo install multiple packages in one command:
sudo apt install package1 package2Additional Useful Commands
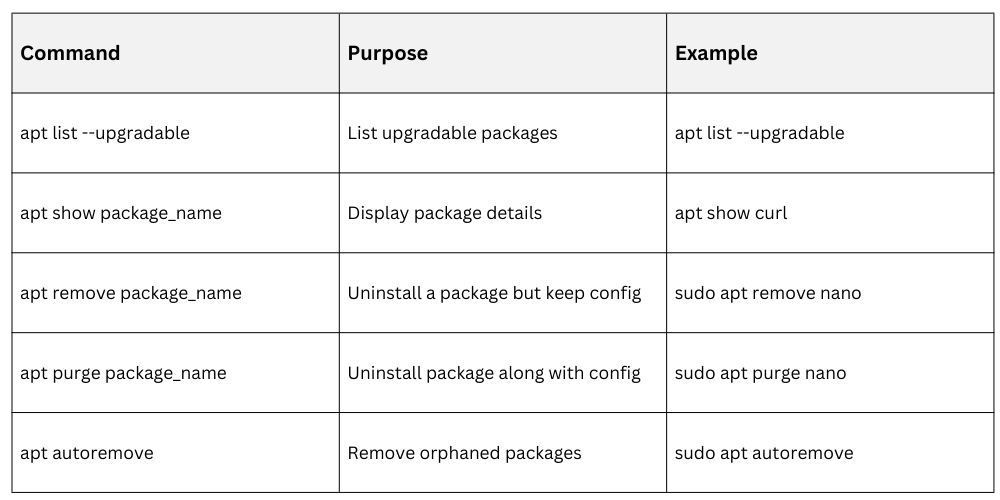
Best Practices
1. Always run sudo apt update before installing or upgrading packages to prevent installing outdated software.
2. Use apt upgrade regularly to keep packages current and secure.
3. For major upgrades or system migrations, use apt full-upgrade or carefully plan upgrades.
4. Regularly clean unused packages with apt autoremove.
5. Use apt show to verify package details before installation.
