Open source software (OSS) has fundamentally transformed the way software is developed, shared, and improved.
Unlike proprietary software, open source software is made available with its source code, enabling anyone to view, modify, and distribute it.
This openness fosters collaboration, innovation, and transparency, making open source critical to modern technology ecosystems.
Open source software powers foundations like Linux, Apache, and Kubernetes, shaping cloud computing, data science, and application development.
What is Open Source Software?
Open source software is software whose source code is freely accessible under licenses that allow users to run, study, change, and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose.
The philosophy emphasizes community collaboration, peer review, and the collective improvement of software without vendor lock-in. Open source projects can range from small utilities to comprehensive systems like entire operating systems.
Principles of Open Source Software
The success of open source software relies on well-defined freedoms and protections. Following are the core principles that govern open source software usage.

Understanding Open Source Licenses
Open source licenses define the legal parameters under which the software is used, modified, and shared. They ensure both the freedom of users and the protection of contributors’ rights. Open source licenses broadly fall into two categories:
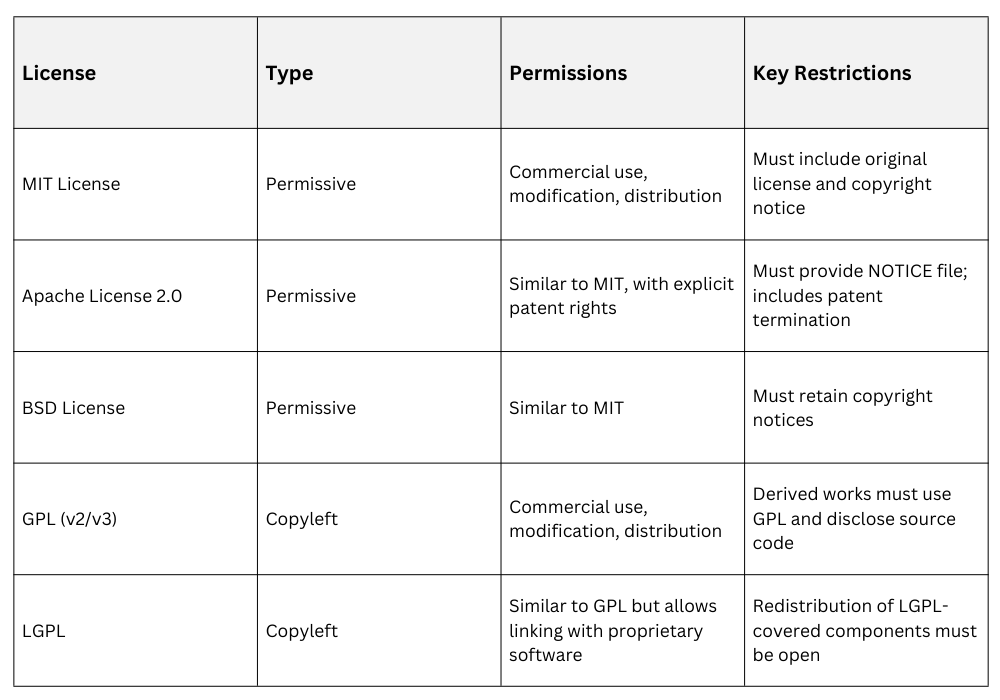
1. Permissive Licenses: These licenses impose minimal restrictions, allowing software to be used in proprietary products.
Examples: MIT License, Apache License 2.0, BSD License
Characteristics: Permit commercial use, modification, distribution; often require attribution and disclaim warranties.
2. Copyleft Licenses: These licenses require derivative works to preserve the same license terms, ensuring continued openness.
Examples: GNU General Public License (GPL), Lesser GPL (LGPL)
Characteristics: Derived works must be distributed under the same license, preventing proprietary forks.
Common Open Source Licenses Comparison
Benefits of Open Source Software
Open source software empowers users with freedom, control, and innovation. Here are the primary benefits that make open source widely adopted.
1. Innovation Acceleration: Collective development advances features and security rapidly.
2. Cost Savings: No licensing fees reduce software acquisition and development costs.
3. Transparency and Security: Open code allows auditing and quick vulnerability patches.
4. Flexibility and Control: Users can customize software to meet specific needs.
5. Community Support: Large ecosystems provide documentation, forums, and shared expertise.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, open source software requires careful governance and oversight. Below is a list of challenges organizations should be mindful of..png) Open Source in Modern IT Landscapes
Open Source in Modern IT Landscapes
Operating systems like Linux, databases like PostgreSQL, web servers like Apache, and orchestration tools like Kubernetes are open source.
Enterprises increasingly adopt open source for mission-critical applications, supported by commercial vendors offering enterprise-grade distributions and service contracts.
Cloud-native development, DevOps, and containerization all heavily rely on open source software.
