Cloud computing relies heavily on compute services, which provide the processing power required to run applications, host websites, and perform complex computations.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers two foundational compute services that serve different use cases: Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and AWS Lambda.
Both are integral to building scalable and efficient cloud applications, but differ in how computing resources are managed and utilized.
Amazon EC2: Virtual Servers in the Cloud
Amazon EC2 provides on-demand, resizable computing capacity in the form of virtual servers called instances. Users can launch and manage these instances to run applications just as they would on physical servers, but with far greater flexibility.
EC2 supports a vast array of instance types optimized for different workloads, such as general-purpose computing, memory-intensive applications, or GPU-based graphics rendering.
Users select an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) that includes the operating system and software configuration for the instance, with options for Linux, Windows, and more.
Key Features of Amazon EC2 include: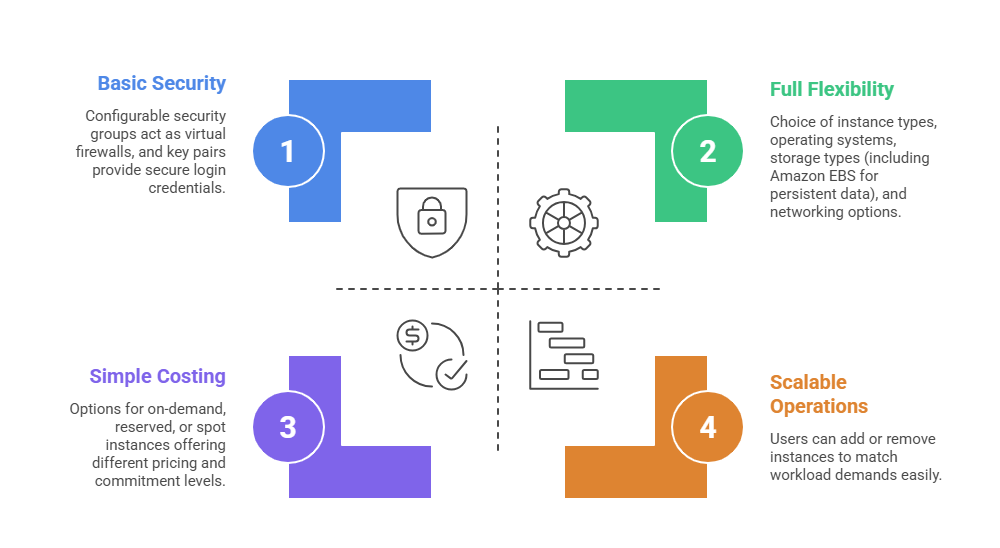
Amazon EC2 is ideal for applications requiring consistent compute power, full control over the operating system, and the ability to install custom software. It forms the backbone of many large, complex cloud solutions.
AWS Lambda: Serverless Computing
AWS Lambda represents a new approach to computing known as serverless computing.
Instead of provisioning and managing servers, developers upload their code (called Lambda functions) to AWS, which automatically handles running and scaling the code in response to triggers like file uploads, database updates, or HTTP requests.
Lambda functions execute only when needed, which means users are charged solely for the compute time consumed, leading to potentially lower costs.
Key Highlights of AWS Lambda include:
1. Event-Driven: Functions execute in direct response to events from AWS services or external sources.
2. No Server Management: AWS manages all infrastructure, including scaling, patching, and fault tolerance.
3. Scalability: Instantly scales from a few requests per day to thousands per second without user intervention.
4. Stateless Execution: Each function invocation is independent, requiring external storage for state if needed.
AWS Lambda suits applications with variable or unpredictable workloads, microservices architectures, or real-time data processing where the overhead of managing servers is impractical.
Amazon EC2 vs. AWS Lambda
| Feature | Amazon EC2 | AWS Lambda |
| Compute Model | Virtual servers (instances) | Serverless event-driven functions |
| Server Management | User managed | Fully managed by AWS |
| Pricing Model | Pay per instance hour/second | Pay per execution time |
| Scaling | Manual or automatic via Auto Scaling | Automatic, instant scaling |
| Use Cases | Long-running applications, full OS control | Event processing, microservices, intermittent workloads |
Class Sessions
Sales Campaign

We have a sales campaign on our promoted courses and products. You can purchase 1 products at a discounted price up to 15% discount.
